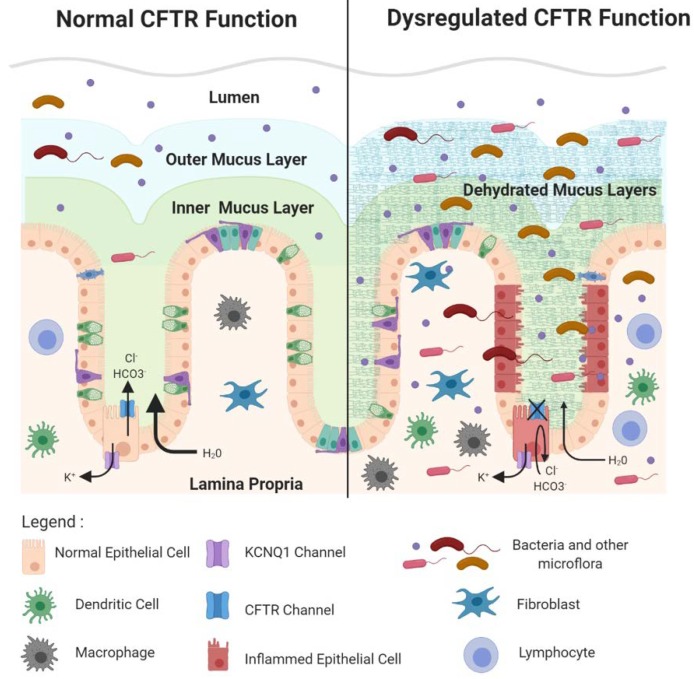
Figure 2.
CFTR deficiency disrupts protective physical barriers and leads to dysbiosis. CFTR deficiency causes a failure of intestinal cell chloride and bicarbonate ion efflux and accompanying water efflux. This results in dehydration of the mucus layer, making it permissive to bacterial passage, and also causing intestinal obstruction. Disruption of the epithelial barrier leads to infiltration of commensal and pathogenic bacteria, inflammation, epithelial tissue damage, and immune cell infiltration. These alterations in the intestinal landscape (mutations, inflammatory signaling) create favorable conditions for CRC initiation and progression. Figure created using BioRender.com.