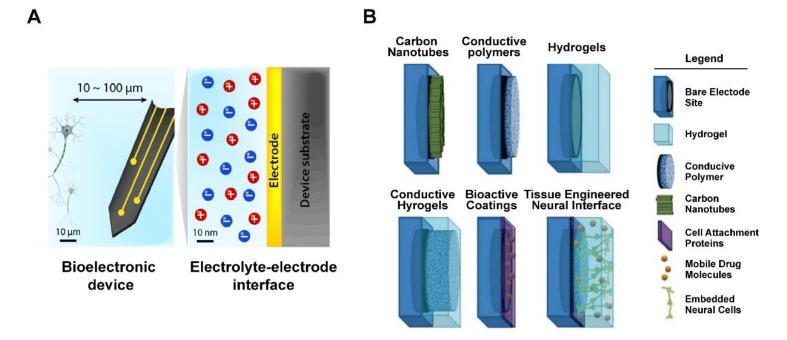
Figure 4.
Schematic of tissue–electrode interfaces. (A) The electrodes of bioelectronic devices are usually implanted within 100 μm of the target tissue, and exchange of electronic signals occurs at a nanoscale electrolyte–electrode interface. Adapted with permission from Hyunwoo et al. [55]. (B) Application of various non-metallic material coating technologies as electrode interface, includes bare electrode site, hydrogel, conductive polymer, carbon nanotubes, cell attachment proteins, mobile drug molecules, and embedded neural cells. Adapted with permission from Aregueta-Robles et al. [57].