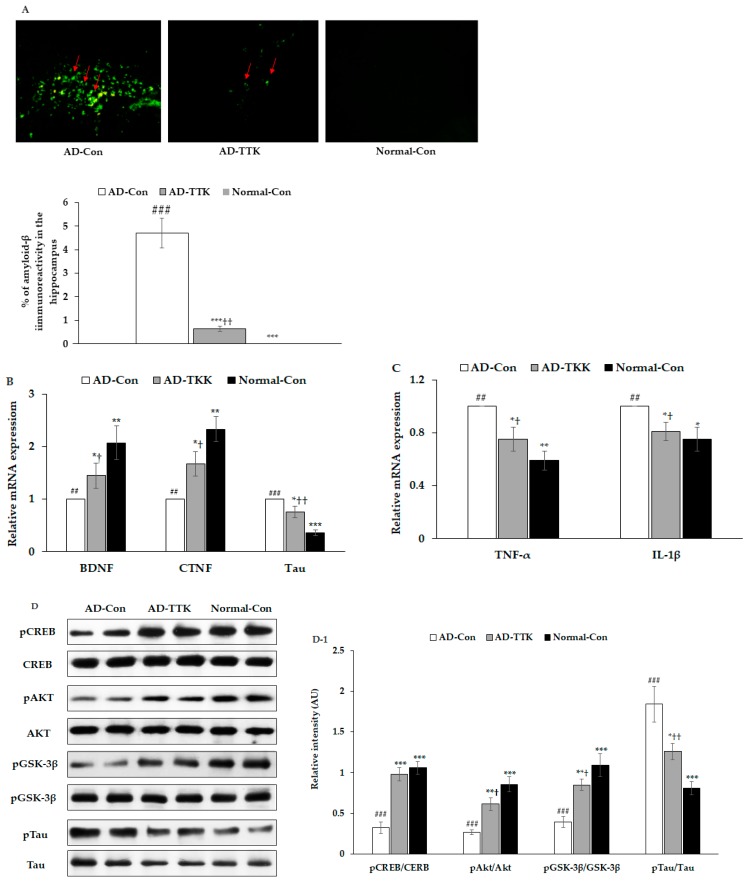
Figure 4.
Amyloid-β deposition, expression of brain growth factor and neuroinflammation and insulin signaling in the hippocampus. (A) Amyloid-β accumulation in the hippocampus by immunohistochemistry staining with amyloid-β antibody (X200). Green fluorescent dots indicated the amyloid-β staining. (B) Hippocampal mRNA expression of BDNF, CNTF, and Tau. (C) Hippocampal mRNA expression of TNF-α and IL-1β. (D,D-1) Hippocampal insulin signaling and its intensity measured by an image analyzer. AD-Con fed 45% fat diet with 0.5% dextrin in AD rats infused intra-CA1 infusion of amyloid-β(25–35), AD-TTK fed 45% fat diet with 0.5% water extract of Tetragonia tetragonioides (TTK) in AD rats, and Normal-Con fed 45% fat diet with 0.5% dextrin in non-AD rats infused intra-CA1 infusion of amyloid-β(35–25). Each bar represents Means ± SD (n = 4). # Significantly different among the groups in one-way ANOVA at p < 0.05, ## p < 0.01 and ### p < 0.001. * Significantly different from AD-Con at p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, and *** p < 0.001 in the Tukey test. † Significantly different from the Normal-Con at p < 0.05 and ††p < 0.01 in the Tukey test.