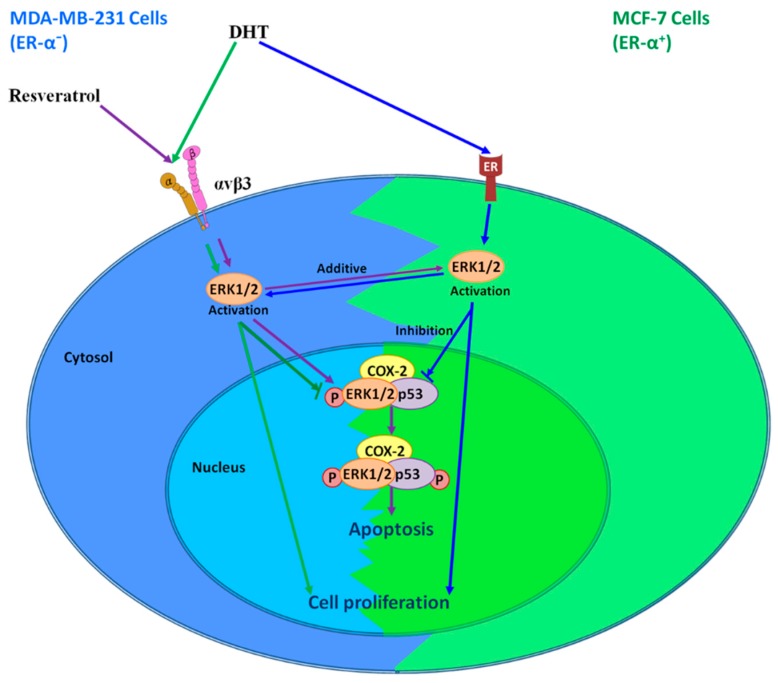
Figure 1.
Signal transduction pathways in the actions of resveratrol and DHT in different breast cancer cells. Extracellular signal-regulated kinases 1/2 (ERK1/2) activated at the plasma membrane are a result of resveratrol binding, and predictably result in cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) expression. Newly-generated COX-2 complexes with phosphorylated ERK1/2 (pERK1/2), is subject to SUMOylation, and then translocates to the nuclear compartment. In the nucleus, COX-2 and modified/activated p53 act as a transcription factor complex, causing the expression of p53-responsive genes. On the other hand, DHT binds to membrane estrogen receptor (ER)-α in ER-α-positive breast cancer cells, while it binds to integrin αvβ3 in ER-α-negative breast cancer cells. DHT activates ERK1/2 and induces cell proliferation. Activated ERK1/2 has discrete functions, depending upon whether activation in cancer cells is a response to resveratrol or DHT. ERK1/2 activation in response to resveratrol causes apoptosis. In contrast, DHT-activated ERK1/2 disrupts resveratrol-induced anti-proliferation. P: phosphorylation. ↓: active, ↓: inhibit.