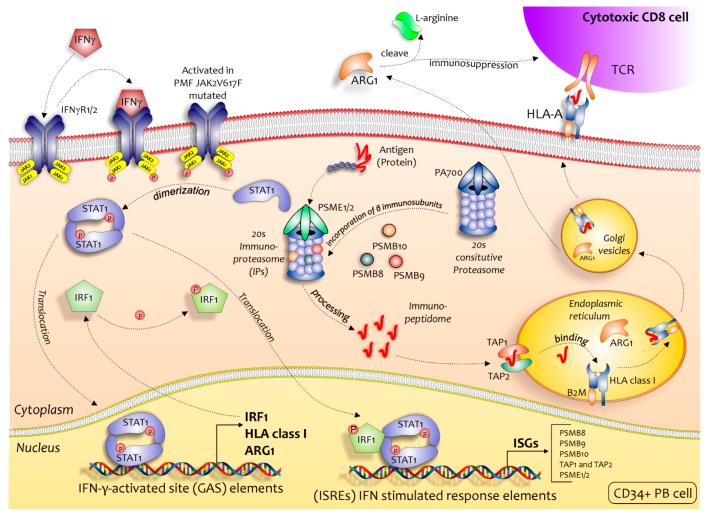
Figure 8.
Regulatory role of the IPs in immune surveillance in PB CD34+ Cells of PMF JAK2V617F mutated patients. The activation of JAK2 pathway, in a classical manner through the binding of IFNG to its receptor (IFNGR1/2) or through the JAK2V617F mutation, induces the expression of the immunoproteasome-specific subunits β1i (PSMB9), β2i (PSMB10), β5i (PSMB8), PA28 (PSME1), and PA28 (PSME2) (via STAT1 and IRF1) that result in the preferred assembly of the immunoproteasome over the regular proteasome. The resulting immuno-peptidome more effectively binds to MHC class I molecules (induced during the activation of JAK2), such that after processing in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) (TAP1 and TAP2) and Golgi apparatus the individual peptides presented on the cell surface can be recognized by T-cell receptors on CD8+ cells, initiating an immune response (increased ARG1 expression is known to result in arginine deficiency, which leads to immunosuppression by impairing lymphocyte proliferation and activation).