Figure 2.
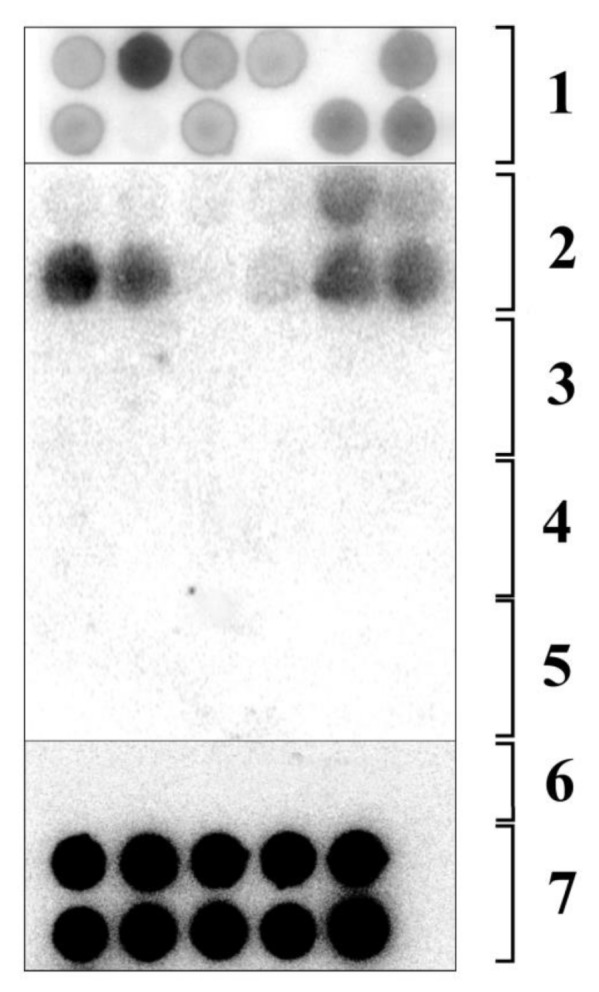
Dot-blot hybridization analysis of AFCVd-inoculated tobaccos and seedlings of F1 generation obtained by reciprocal crossings of AFCVd-infected plants and healthy controls. The dot blot was performed using oligoprime-labeled viroid cDNAs (see Materials and Methods for further details). Row 1, results of biolistic inoculation of N. tabacum with AFCVd RNA partly-purified from infected N. benthamiana (Table 1, row 3), eight weeks post inoculation (p. i.); row 2, AFCVd signals from N. benthamiana inoculated with raw RNA extract using Carborundum method, four weeks p. i.; row 3, 45 day old plants from seeds obtained by crossing of AFCVd-infected parental plants; row 4, 45 day old plants from seeds obtained by crossing uninfected control plants with AFCVd-infected parental plants; row 5, 45 day old plants from seeds obtained by crossing of AFCVd-infected parental plants with uninfected control plants; row 6, healthy controls; row 7, AFCVd signal in leaves of tobacco transformed with a plant vector containing infectious dimeric AFCVd driven from p35S. In rows 1–6, six samples, and in row 7, only five samples were spotted to one row.
