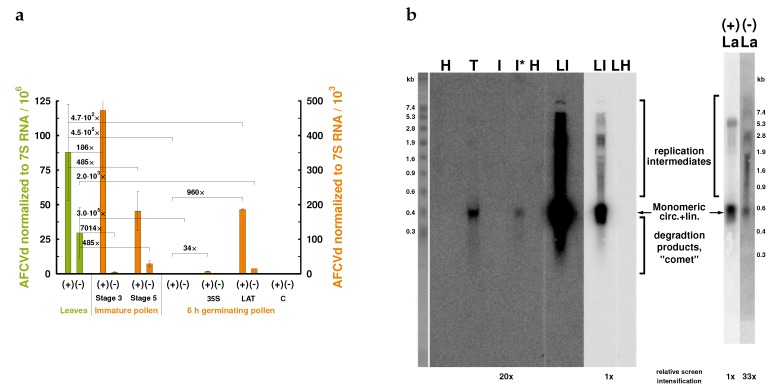
Figure 3.
Levels of AFCVd in developing, mature and germinating pollen. (a) Strand-specific RT-qPCR profiles of AFCVd infection in different N. tabacum tissues. Total RNA was isolated from infected leaves and pollen at different stages, reverse transcribed for (+) or (−) AFCVd strands and their relative levels were assayed using qPCR and normalized to 7SL RNA. (+), (−), AFCVd sequences of (+) and (−) polarity, respectively; 35S, transformed pollen with 35S:AFCVd vector; LAT, plant transformed with AFCVd dimer under pLAT52 promoter; C, healthy control. (b) Northern blot analysis of AFCVd intermediates. Analysis was performed using 35 μg of total RNA per lane isolated from AFCVd infected N. tabacum tissues collected within the interval 90–120 dpi. Samples were probed either by [32P-dCTP]-labeled viroid cDNA or by [32P-dUTP]-labeled strand-specific RNA probes in lanes designated (+) and (−) with 1 × 106 cpm per 1 mL of hybridization solution and hybridized as described in Materials and Methods. Membranes were scanned after 24 h exposure, relative screen intensification is given at the bottom of the figure. The marker ladder on the left is the ethidium bromide-stained RNA III marker (Boehringer Mannheim). The position of AFCVd monomer is indicated by an arrow. H and T, RNA from healthy and transformed 6 h-grown pollen tubes, respectively; I, RNA from infected 6 h-grown pollen tubes; I*, RNA from infected 6 h-grown pollen tubes after sample concentration by precipitation of LiCl-soluble RNA; LI, RNA from infected tobacco upper leaves; LH, RNA from healthy tobacco upper leaves; La, AFCVd in mature pollen transformed with plant vector pLAT56:bZIP18:AFCVd as detected by strand-specific probes.