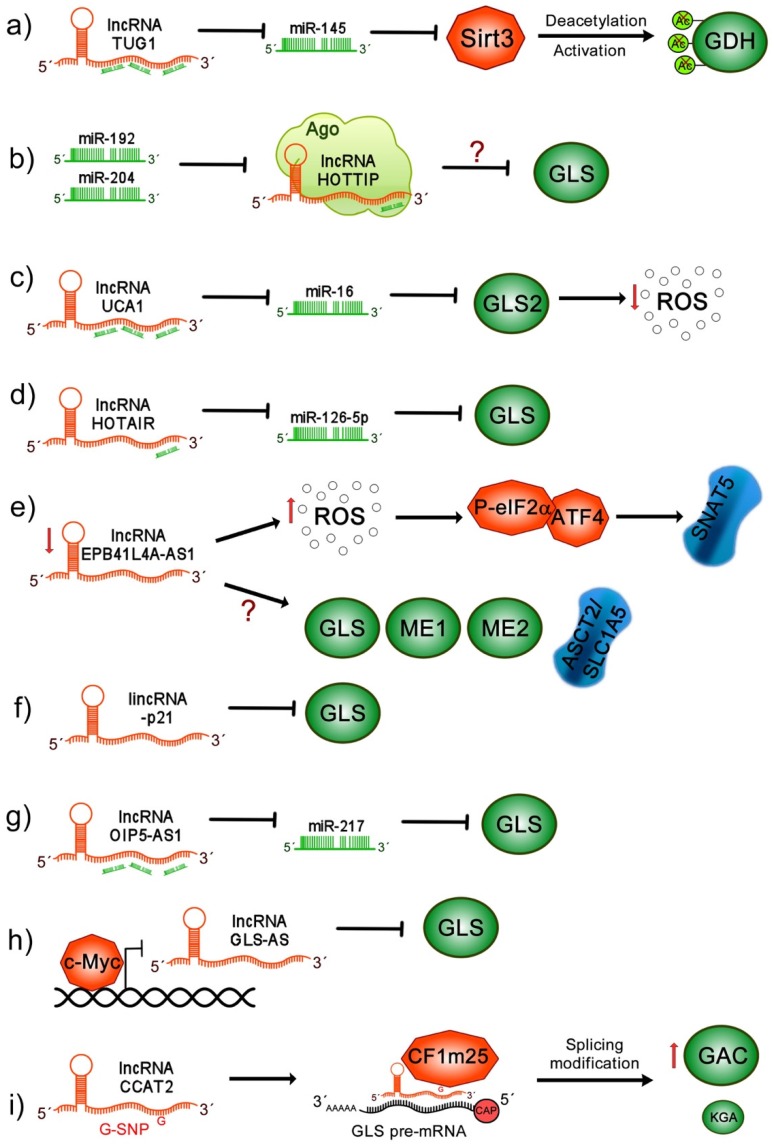
Figure 3.
lncRNAs affect glutaminolysis pathway in cancer. (a) lncRNA taurine upregulated gene 1 (TUG1) acts as an miR-145 sponge, preventing Sirt3 mRNA degradation, which promotes glutamate dehydrogenase (GDH) deacetylation and its consequent activation; (b) miR-192 and miR-204 induce the suppression of lncRNA homeobox A (HOXA) distal transcript antisense RNA (HOTTIP) at the posttranscriptional level through Argonaute 2, inhibiting GLS expression; (c) lncRNA urothelial carcinoma associated 1 (UCA1) acts as sponge for miR-16, impairing the canonical binding of miR-16 to GLS2, promoting upregulation of GLS impacting in ROS reduction; (d) lncRNA homeobox (HOX) transcript antisense intergenic RNA (HOTAIR) functions as a ceRNA for miR-126-5p, modulating GLS expression; (e) low levels of lncRNA erythrocyte membrane protein band 4.1 like 4A (EPB41L4A)-AS1 induces high levels of reactive oxygen species (ROS), activation of P-eIF2α/ATF4 complex and overexpression of SNAT5 transporter. Moreover, through unknown mechanisms, EPB41L4A-AS1 leads an increase in ASCT2, GLS and ME1/2, leading to the increase in glutamine consumption; (f) long intergenic non-coding RNA p21 (lincRNA-p21) decreases GLS transcript and protein levels; (g) lncRNA opa-interacting protein 5 antisense transcript 1 (OIP5-AS1) acts as an miR-217 sponge upregulating GLS expression, contributing to the activation of glutaminolysis; (h) c-Myc inhibits lncRNA GLS-AS transcription, allowing the GLS stabilization; however, when lncRNA antisense lncRNA of glutaminase (GLS-AS) is expressed, mGSL is inhibited through the Adenosine Deaminase RNA Specific (ADAR)/dicer-dependent RNA interference; (i) lncRNA colon cancer associated transcript 2 (CCAT2) G allele binds to the CFIm25 subunit that interacts with GLS pre-mRNA and allows its alternative splicing, favoring the expression of glutaminase C (GAC) rather than kidney-type glutaminase (KGA), both GLS isoforms.