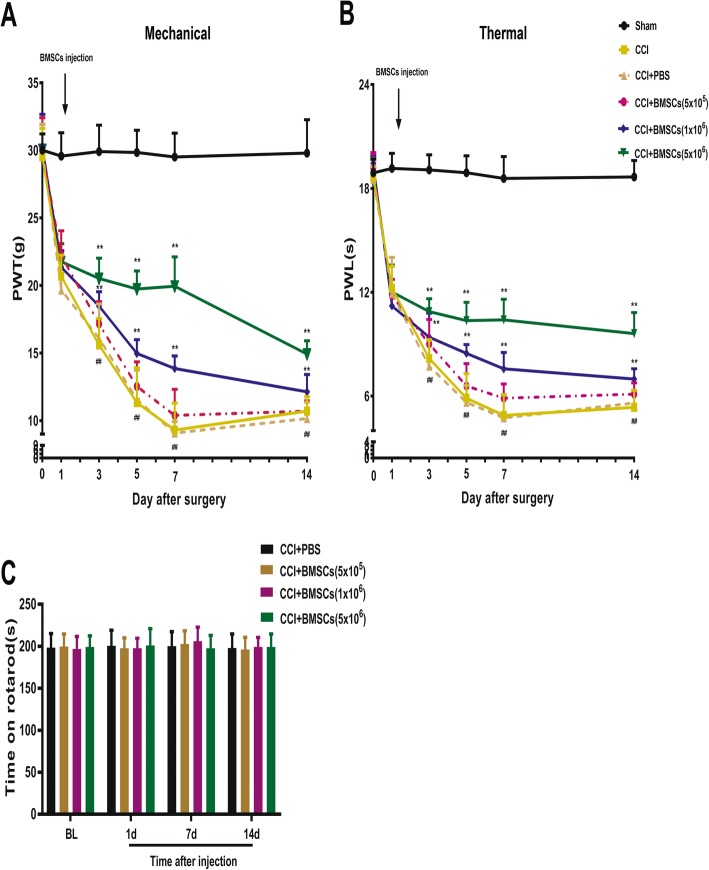
Fig. 2.
Inhibition of CCI-induced neuropathic pain in rats by a single intrathecal injection of BMSCs. Paw withdrawal mechanical threshold (a) and paw withdrawal thermal latency (b) were reduced after CCI in rats. In contrast, early intrathecal treatment (1 day after sham or CCI surgery) with BMSCs recovered mechanical allodynia and thermal hyperalgesia in a dose-dependent manner in CCI rats. c Rotarod test for the evaluation of motor function. Arrows in (a, b) indicated the time of BMSCs injection. The data are expressed as the means ± SD (n = 8 in each group). **P < 0.01 versus the CCI group; ##P < 0.01 versus the Sham group. Statistical significance was determined by two-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) with post hoc Tukey test