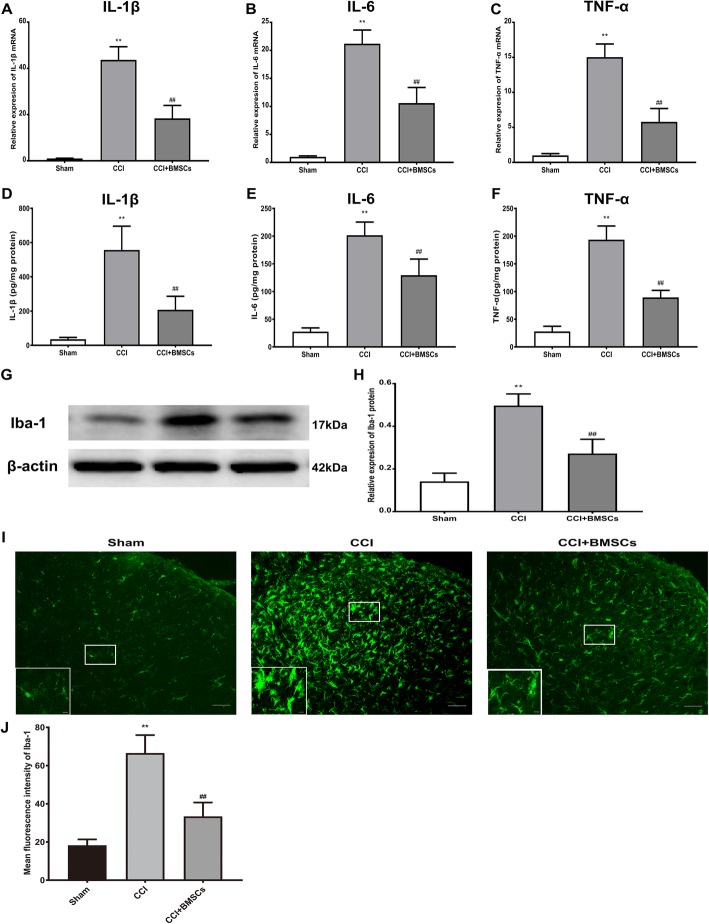
Fig. 4.
BMSCs suppressed neuropathic pain-induced production of pro-inflammatory cytokines and activation of microglia in rat spinal cord dorsal horn. a–f Real-time RT-PCR and ELISA data showed that CCI induced an increase of IL-1β, IL-6, and TNF-α in the ipsilateral spinal cord dorsal horn of rat, while intrathecal injection of BMSCs inhibited the changes of IL-1β, IL-6, and TNF-α in the rat ipsilateral spinal cord dorsal horn. g Representative image of protein level of Iba-1 in the rat ipsilateral spinal cord dorsal horn. h Quantitative analysis of western blotting results showed that CCI surgery significantly increased the expression of Iba-1, in contrast, intrathecal delivery of BMSCs decreased the expression of Iba-1 in the rat ipsilateral spinal cord dorsal horn. i Representative immunohistological staining showed that BMSCs inhibited the CCI-induced upregulation of microglia marker Iba-1 in the rat ipsilateral spinal cord dorsal horn. Scale bar: 50 μm; 10 μm (inserts). j Quantitative analysis of mean fluorescence intensity of Iba-1. The data are expressed as the means ± SD (n = 8 in each group). **P < 0.01 versus the sham group. ##P < 0.01 versus the CCI group. Statistical significance was determined by one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) with post hoc Tukey test