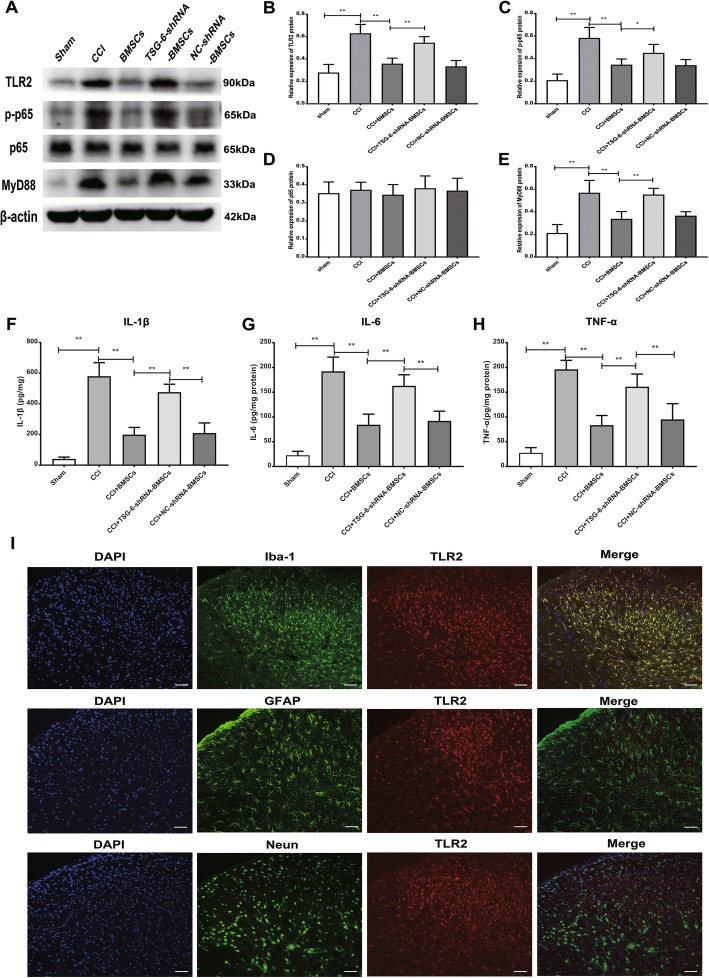
Fig. 7.
BMSCs down-regulated the TLR2/MyD88/NF-κB signaling pathway and reduced the protein levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines in CCI rats by releasing TSG-6. a Representative image of protein levels of TLR2, MyD88, p-p65, p65 in the ipsilateral spinal cord dorsal horn. b–e Quantitative analysis of western blotting results showed that BMSCs intrathecal delivery significantly inhibited the protein levels of TLR2, MyD88, p-p65 in the CCI rat ipsilateral spinal cord dorsal horn, in contrast, the TSG-6-shRNA transfection abrogated the inhibitory effect of BMSCs on the expression of these proteins in the CCI rat ipsilateral spinal cord dorsal horn. BMSCs intrathecal injection significantly reduced the protein contents of IL-1β (f), IL-6 (g), and TNF-α (h) in the CCI rat ipsilateral spinal cord dorsal horn, while the inhibitory effect of BMSCs on the production of these pro-inflammatory cytokines was weakened after TSG-6 was knock down. i TLR2 immunosignals were co-localized with signals of Iba-1-positive microglia, but not with signals of GFAP-positive astrocytes or NeuN-positive neurons in the CCI rat ipsilateral spinal cord dorsal horn. Scale bar: 50 μm. The data are expressed as the means ± SD (n = 8 in each group). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01. Statistical significance was determined by one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) with post hoc Tukey test