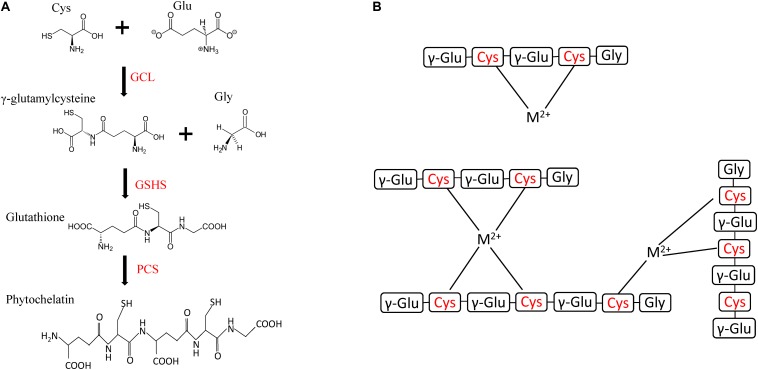
FIGURE 3.
Structure and biosynthetic pathways of glutathione (GSH) and phytochelatin (PC). Three-letter abbreviations correspond to amino acid codes. (A) The biosynthetic pathway of GSH and PC consists of two and three reactions, respectively. First, a cysteine unit binds to the carboxylic group of the side chain of glutamic acid residue to form γ-glutamylcysteine, and this reaction is catalyzed by glutamate–cysteine ligase (GCL), then γ-glutamylcysteine binds to a glycine residue to form glutathione, and glutathione synthetase (GSHS) catalyses this reaction. PC-synthase (PCS) might then bind two or more GSH units to form phytochelatins. (B) Example of PC–metal complexes for divalent cations. M2+ denotes bivalent metal cations, whereas cysteine residues are indicated in red.