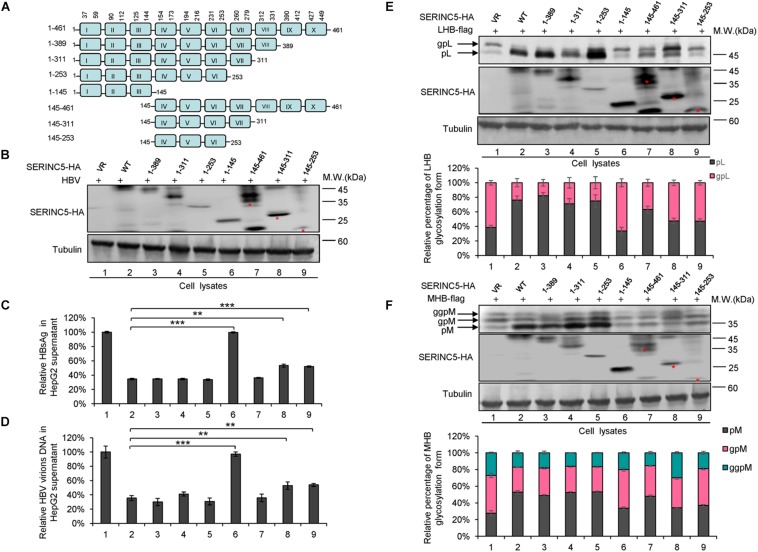
FIGURE 7.
The functional domain of serine incorporator 5 (SERINC5) required for hepatitis B virus (HBV) inhibition. (A) Schematic diagram of the transmembrane domains of SERINC5 and its mutants. The structure was predicted by Transmembrane Prediction using Hidden Marow Models (TMHMM) on a public server (http://www.cbs.dtu.dk/services/TMHMM-2.0/). (B–D) The effect of wild-type (WT) SERINC5 and SERINC5 truncated mutants on hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) and HBV virion secretion. HepG2 cells were co-transfected as indicated. (B) Immunoblot analysis of SERINC5 and SERINC5 mutants using anti-HA antibody, tubulin served as a loading control. (C) The culture supernatants were monitored by HBsAg ELISA. HBsAg in the absence of SERINC5 was set as 100%. (D) Virion DNA from culture supernatant was detected by qPCR following the immunoprecipitation with anti-S Abs conjugated to protein G beads. HBV virion DNA in the absence of SERINC5 was set as 100% (n = 3, mean ± SD, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, paired t-test). The effect of WT SERINC5 and SERINC5 mutants on the glycosylation of LHB (E) and MHB (F) proteins. HEK293T cells were co-transfected as indicated and then harvested for immunoblot analysis 48 h post-transfection. Immunoblot analysis of SERINC5, LHB, and MHB expression using anti-HA or anti-flag antibodies. The glycosylated (gp or ggp) and non-glycosylated (p) forms of LHB (L), and MHB (M) proteins are indicated. Tubulin served as a loading control. Quantitation of bands corresponding to the proteins of interest was performed using the ImageJ software and was shown below each panel (n = 3, mean ± SD).