Figure 1.
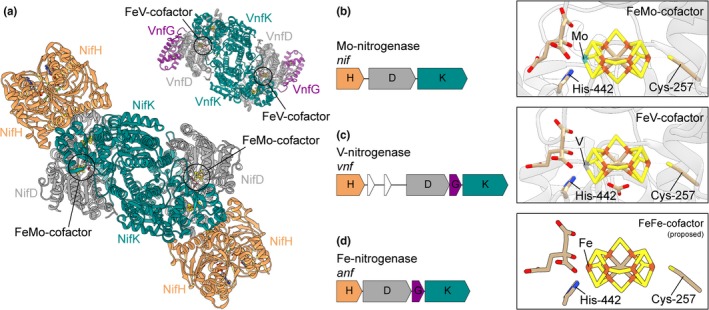
Structure and genetics of the three nitrogenase forms. (a) Structure of the A. vinelandii Mo‐nitrogenase enzyme complex (NifHDK; PDB http://www.rcsb.org/pdb/search/structidSearch.do?structureId=1M34; Schmid et al., 2002) and V‐nitrogenase VFe protein component (VnfDGK; PDB http://www.rcsb.org/pdb/search/structidSearch.do?structureId=5N6Y; Sippel & Einsle, 2017) (Fe‐nitrogenase structure not previously published). The active‐site FeMo‐cofactor of Mo‐nitrogenase and FeV‐cofactor of V‐nitrogenase are circled. (b–d) Catalytic genes and cofactor structures of A. vinelandii Mo‐nitrogenase (b; PDB http://www.rcsb.org/pdb/search/structidSearch.do?structureId=3U7Q; (Spatzal et al., 2011), V‐nitrogenase (c; PDB http://www.rcsb.org/pdb/search/structidSearch.do?structureId=5N6Y; Sippel & Einsle, 2017), and Fe‐nitrogenase (d; proposed structure; Harris, Lukoyanov, et al., 2018). Residue numbering from aligned A. vinelandii NifD. Cofactor atom coloring is as follows: C, tan; Fe, rust; Mo, cyan; N, blue; O, red; S, yellow
