Figure 1.
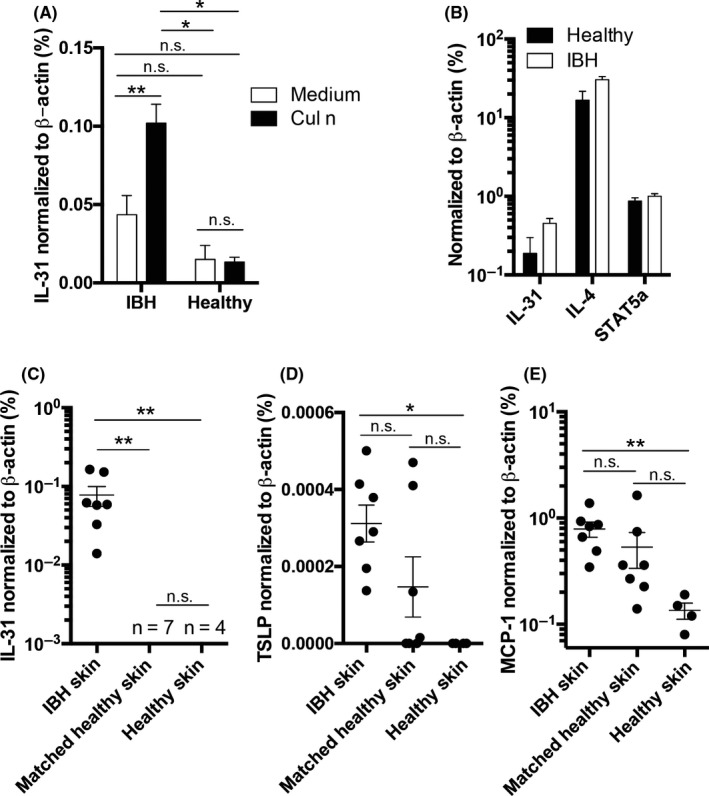
IL‐31 expression in IBH‐affected skin and allergen‐stimulated PBMCs. A and B, Culicoides nubeculosus (Cul n) (A) or Con A (B) allergen extract stimulated PBMCs from IBH‐affected horses (IBH, n = 19) and healthy horses (Healthy, n = 3). A, Percentage of eIL‐31 expression levels relative to eβ‐actin levels upon Cul n stimulation. B, Percentage of eIL‐31, eIL‐4, and Stat5a expression levels relative to eβ‐actin levels upon Con A stimulation. C, D, & E. Two mm skin punch biopsies from IBH‐affected skin (n = 7), healthy skin from IBH‐affected horses (n = 7), and healthy skin from healthy non‐IBH horses (n = 4). Quantification of eIL‐31 (C), eTSLP (D), and MCP‐1 (E) levels by qPCR shown as percent expression of eβ‐actin housekeeping gene, of skin biopsies taken from IBH lesion sites (n = 7), matched healthy skin from the same horses (n = 7), and healthy skin from healthy horses (n = 4)
