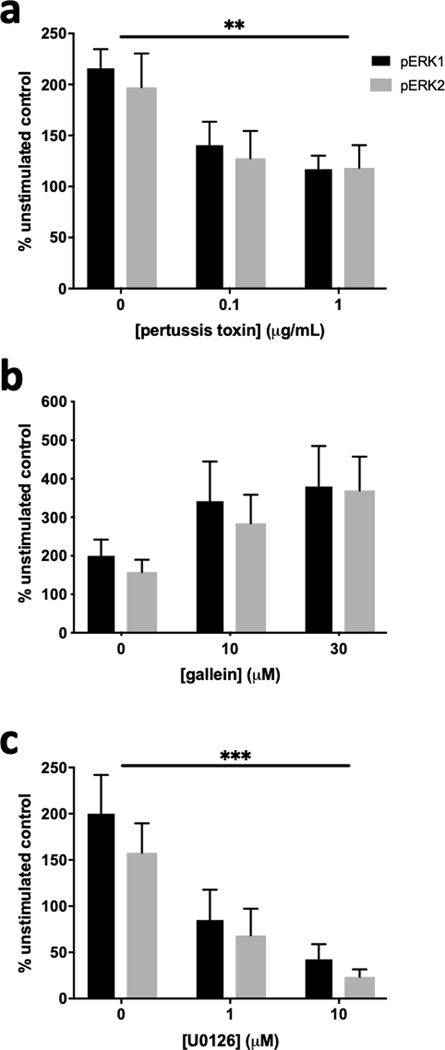
Figure 5. Phosphorylation of ERK1/2 by 5-HT1B receptors is sensitive to pertussis toxin and U0126 but not gallein.
N2A-1B cells were pretreated for one hour with inhibitors prior to treatment with 100 nM CP-94253 for ten minutes and compared to unstimulated N2A-1B control cells treated with vehicle (PBS). (a) 5-HT1B-mediated phosphorylation of ERK1/2 was blocked by pertussis toxin (inhibitor effect: F2,18 = 7.98, p = 0.0033). (b) 5-HT1B-mediated phosphorylation of ERK1/2 was not sensitive gallein (inhibitor effect: F2,12 = 3.198, p = 0.077). (c) 5-HT1B-mediated phosphorylation of ERK1/2 was blocked by the MEK1/2 inhibitor U0126 (inhibitor effect: F2,12 = 13.34, p = 0.0009). Data are expressed as the percent change in pERK signal compared to the no agonist control from each independent biological replicate. Error bars represent SEM and data are averages of 3–4 independent biological replicates for each experiment (two-way ANOVA; ***p < 0.001, **p < 0.01).