Figure 5.
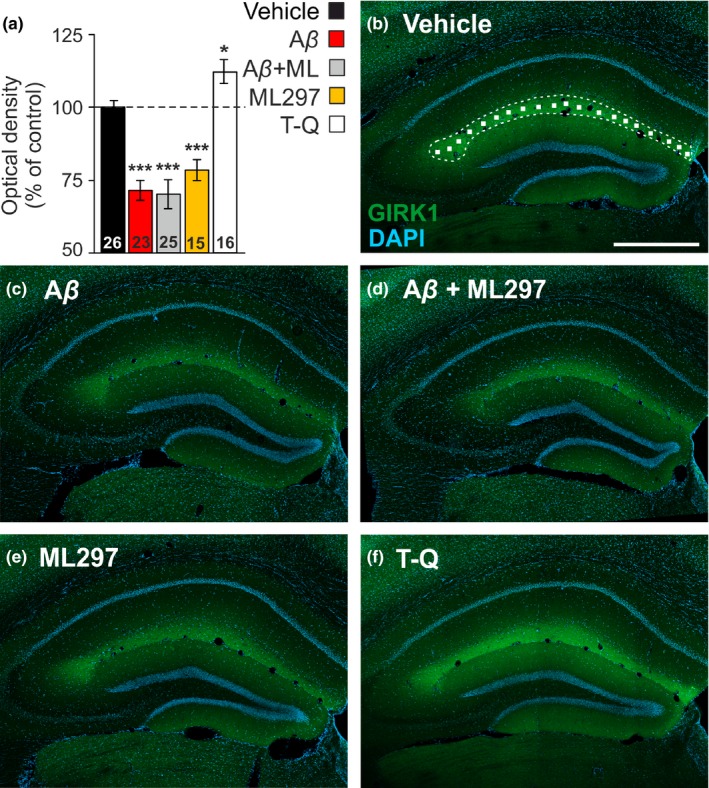
Hippocampal G‐protein‐gated inwardly rectifying potassium channels (GirK) protein pattern is altered by amyloid‐β (Aβ)1–42 in vivo. (a) Bar plots showing GIRK1 immunostaining intensity (measured as optical density), as percentage of control (vehicle) values (dashed line, 100%) in the stratum lacunosum‐moleculare of the dorsal hippocampus in intracerebroventricular (i.c.v.)‐injected mice with vehicle (n = 7 animals), Aβ1–42 (n = 6), Aβ1–42 + ML297 (n = 6), ML297 (n = 4) or tertiapin‐Q (TQ) (n = 4). Number of hippocampal sections for each condition (n = 15–26 slices) is indicated in the corresponding bar. Differences versus. control (vehicle) are indicated by asterisks (*p < .05; ***p < .001). (b) Confocal fluorescence photomicrograph showing the distribution of GIRK1 subunit (green labeling), with intense immunolabeling in the stratum lacunosum‐moleculare, and DAPI stained cells (blue labeling) in the dorsal hippocampus of a representative vehicle‐injected mouse. The image illustrates how random 15 × 15 µm squares were distributed through the stratum lacunosum‐moleculare to measure GIRK1 optical density. Calibration bar: 500 µm (c–f) Representative confocal microscopy images showing GIRK1 immunostaining in i.c.v.‐injected mice with Aβ1–42 (c), Aβ1–42 + ML297 (d), ML297 (e), and TQ (f). Calibration bar in (b) also applies for (c–f)
