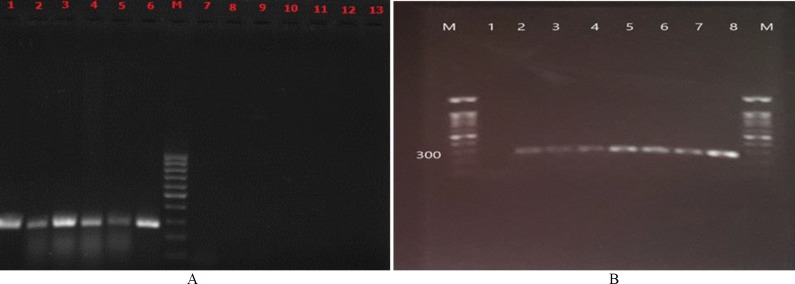
Figure 1.
(A) Electrophoresis patterns of pan-Candida polymerase chain reaction using DNA template; lane 1) Candida albicans (ATCC 5982), lane 2) Candida tropicalis (ATCC 750), lane 3) Candida parapsilosis (ATCC 4344), lane 4) Candida albicans (ATCC 64553), lane 5) Candida tropicalis (CBS 94), lane 6) Candida krusei (ATCC 6258), lane 7) Aspergillus fumigatus (ATCC 14110), lane 8) Aspergillus flavus (ATCC 64025), lane 9) penicillium chrysogenum (clinical isolate), lane 10) Fusarium solani (clinical isolate), lane 11) Cryptococcus neoformans (ATCC 9011), lane 12) Escherichia coli (ATCC 43894), lane 13) negative control (sterile distilled water), and lane M) a 100-bp molecular size marker; (B) Determine the detection limit of this pan-Candida primers; lane 1) negative control (sterile distilled water), lane2) 2-7 nails treated with serially diluted standard strain (C. albicans (ATCC 5982)) at a concentration of 101-106 CFU/ml, lane 8 positive control (C. parapsilosis (ATCC 4344)) and lane M) a 100-bp molecular size marker