Extended Data Fig. 7 |. Nuclear positioning during amoeboid cell migration.
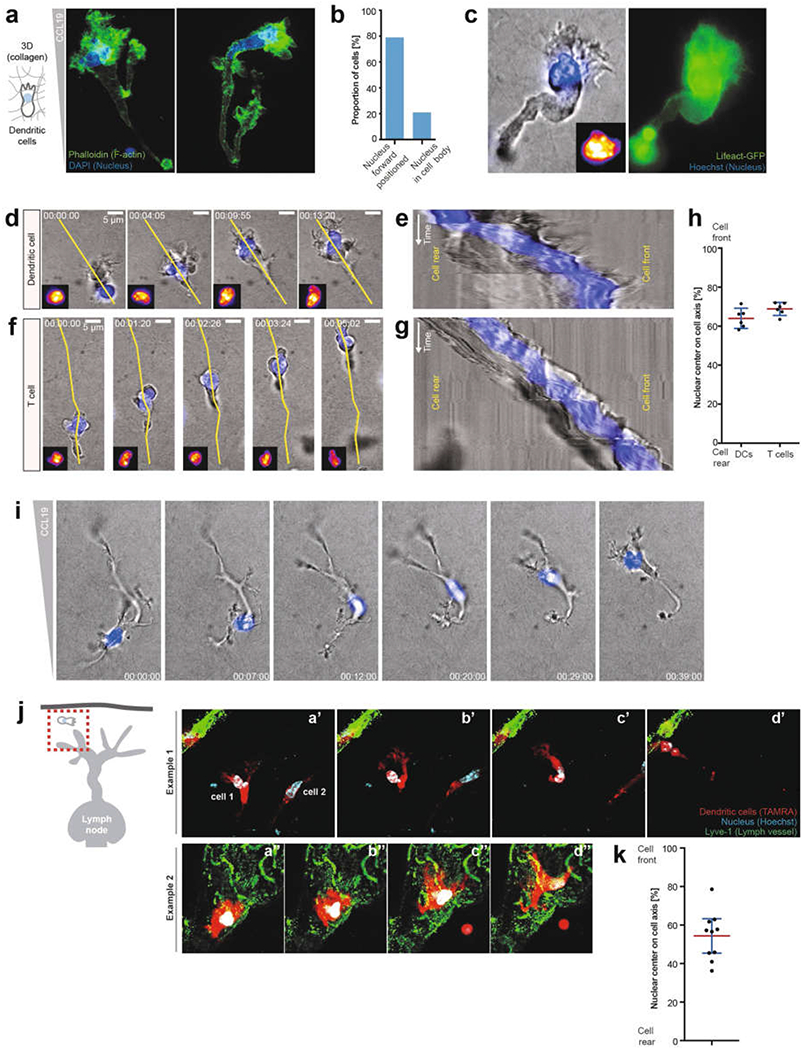
a, DCs migrating in a 3D collagen matrix along a CCL19 gradient, fixed with paraformaldehyde and stained with phalloidin (green) and DAPI (blue). Two examples are shown; note the nuclear positioning close to the cell front directly behind the F-actin-rich lamellipodium (3 experiments). b, Quantification of the nuclear location in a (62 cells). c, Live-cell imaging of a DC labelled with LifeAct–GFP (green) and Hoechst nuclear stain (blue), showing nuclear positioning close to the cell front directly behind the actin-rich lamellipodium (3 experiments). d Temporal analysis of nuclear positioning during DC migration in a 3D collagen matrix along a CCL19 gradient (yellow line depicts the kymographic axis in e). Note that the cell polarizes at time point 0, after which the nucleus quickly positions close to the cell front (3 experiments). e, Kymographic analysis of d (3 experiments). f, Temporal analysis of nuclear positioning during T cell migration in a 3D collagen matrix along a CCL19 gradient (yellow line depicts the kymographic axis in e) (3 experiments). g, Kymographic analysis of f. Note the nuclear positioning close to the cell front (3 experiments). h, Quantification of nuclear positioning along the cell axis (n = 6 cells; data are mean ± 95% CI). i, Representative of a repolarizing DC (the former front becomes the new back edge) migrating in a 3D collagen matrix along a CCL19 gradient. Note that the nucleus translocates through the entire cell body to position to the new cell front (n = 3 experiments). j, Ex vivo DC (TAMRA, red) migration in mouse skin ear explants (scheme, left) towards lymphatic vessels (LYVE1, green). Two exemplary image sequences (n = 3 experiments). k, Quantification of nuclear positioning along the cell axis in j (n = 10 cells; data are mean ± 95% CI).
