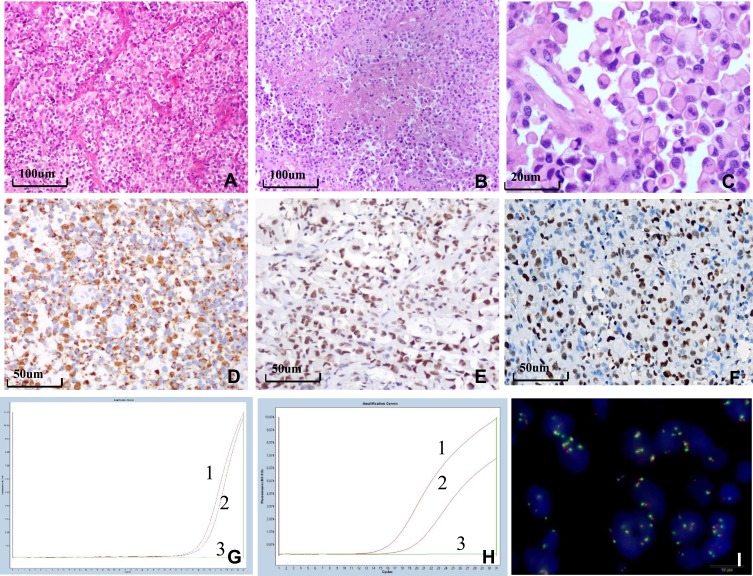
Figure 2.
Histological, immunohistochemical, and molecular findings of E-GBM. (A) Epithelioid and rhabdoid cells were arranged in patches or were in close proximity with rich vasculature with thin walls (×100). (B) The tumor exhibited zonal necrosis (×100). (C) Epithelioid and rhabdoid cells were round or oval, containing laterally located oval to pleomorphically shaped nuclei and abundant and homogeneously eosinophilic cytoplasm. Mitoses were easily observed (×400). (D) Epithelioid cells were positive for GFAP, INI-1 (E) and EZH2 (F) (×200). (G) MGMT-MSP revealed MGMT methylation in case 6. (H) HRM-PCR revealed a BRAF V600E mutation in case 1. Curve 1 shows the positive control, curve 2 shows the tumor specimen, and curve 3 shows the negative control. (I) EGFR FISH revealed a high level of polysomy in the tumor in case 7.
Abbreviations: E-GBM, epithelioid glioblastoma; GFAP, glial fibrillary acidic protein; SMARCB1/INI-1, SWI/SNF-related, matrix-associated, actin-dependent regulator of chromatin, subfamily b, member 1; EZH2, enhancer of zeste 2; MGMT, O-6-methylguanine-DNA methyltransferase; MSP, methylation-specific polymerase chain reaction; HRM-PCR, high-resolution melt polymerase chain reaction; BRAF, v-raf murine sarcoma viral oncogene homolog B1; EGFR, epithelial growth factor receptor; FISH, fluorescence in situ hybridization.