Fig 4. FBW7 is ubiquitinated with K48-Ub and degraded by the proteasome.
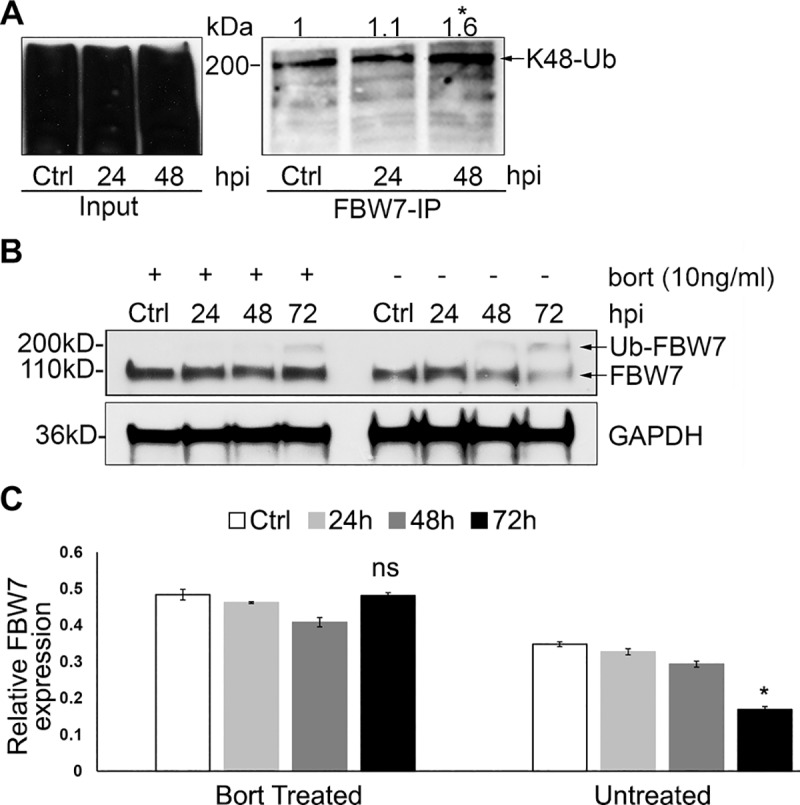
A. Immunoprecipitation of K48-Ub FBW7 from uninfected and E. chaffeensis-infected THP-1 cells demonstrating increased levels of FBW7 K48-Ub. Lysates were treated with NEM (N-ethylmaleimide, equal mass amount to whole cell lysates used) and bortezomib (10ng/ml, 10 h) to prevent deubiquitination and proteasome degradation. Anti-K48-Ub antibody was used to pull down all K48-Ub conjugated proteins. Basal levels of K48-Ub FBW7 at ~200 kDA are observed indicating FBW7 undergoes K48-Ub as a mechanism of protein regulation and turnover. Densitometry values of K48-Ub-FBW7 bands were denoted on top of each band for every time point, and a p<0.05 significance comparing 48 hpi to uninfected control (0 hpi) was calculated from three experiments (n = 3). B. Western immunoblots demonstrating the effect of bortezomib (bort, 26S proteasome inhibitor) on FBW7 during infection. Whole cell lysates were obtained from both bort-treated (10ng/ml, 10 h) and untreated groups infected with cell-free E. chaffeensis and uninfected controls at 24, 48 and 72 hpi. Uninfected cells were harvested at the same time points (24, 48 and 72 hpi) with only a single time point (ctrl) shown in the figure as significant differences were not observed among uninfected cells. FBW7 levels remained unchanged during infection in the bort-treated group; however, there was a temporal reduction of FBW7 levels in untreated group, demonstrating FBW7 proteasomal degradation during infection. C. Densitometry of Western immunoblots (B) performed using image J. Statistical analysis was done by comparing data from infected cells to control cells at respective time points (n = 3). A p<0.05 significance was determined for FBW7 level at 72 hpi in the untreated group compared to uninfected control in the same group.
