Figure 1.
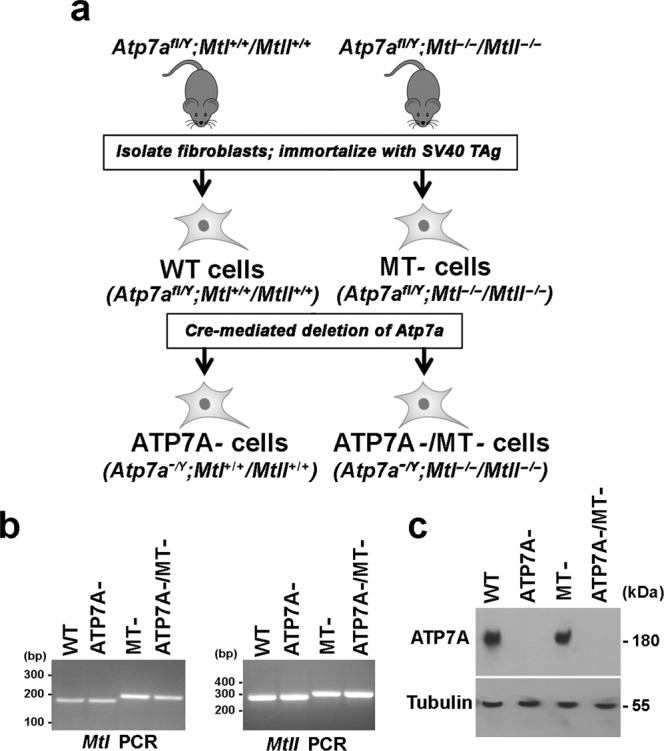
Derivation and characterization of cell lines lacking Atp7a, MtI and MtII genes. (a) Primary fibroblasts were isolated from the lungs of Atp7afl/Y;MtI+/+/MtII+/+ and Atp7afl/Y;MtI−/−/MtII−/− mice and then immortalized by transfection with a plasmid expressing the SV40 large T antigen (SV40 Tag) resulting in WT and MT- cells, respectively. An adenoviral vector encoding CRE recombinase was used to delete Atp7a in WT and MT- cells to obtain ATP7A- and ATP7A-/MT- cells, respectively. (b) PCR analysis of genomic DNA was used to confirm deletion of MtI and MtII genes in both the MT- and ATP7A-/MT- cell lines. Expected PCR product sizes: MtI gene (WT = 161 bp; knockout = 176 bp); MtII gene (WT = 282 bp; knockout = 299 bp). (c) Immunoblot analysis was used to confirm the loss of ATP7A protein in both ATP7A- and ATP7A-/MT- cell lines. Tubulin was detected as a loading control. Images of full-length gels and immunoblots are provided in the supplementary data.
