Table 1.
Condition optimization.
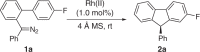 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Entrya | Rh(II) | Solvent | Yield (%)b | Ee (%)c |
| 1 | Rh2(S-TCPTTL)4 | DCM | 91 | 60 |
| 2 | Rh2(S-TCPTTL)4 | DCE | 90 | 63 |
| 3 | Rh2(S-TCPTTL)4 | Toluene | 85 | 75 |
| 4 | Rh2(S-TCPTTL)4 | Hexane | 90 | 62 |
| 5 | Rh2(S-TCPTTL)4 | TBME | 92 | 82 |
| 6d | Rh2(S-TCPTTL)4 | TBME | 80 | 81 |
| 7d | Rh2(S-PTTL)4 | TBME | 82 | 15 |
| 8 | Rh2(S-NTTL)4 | TBME | 90 | 65 |
| 9 | Rh2(S-TBPTTL)4 | TBME | 92 | 70 |
| 10 | Rh2(S-TFPTTL)4 | TBME | 90 | 99 |
| 11 | Rh2(S-PTPA)4 | TBME | 75 | 5 |
| 12 | Rh2(S-PTA)4 | TBME | 72 | 2 |
| 13 | Rh2(S-DOSP)4 | TBME | 90 | 13 |
| 14d | Rh2(S-PTAD)4 | TBME | 92 | 25 |
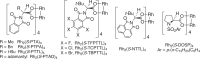 | ||||
DCM dichloromethane, DCE 1,2-dichloroethane, TBME tert-butyl methyl ether.
aThe reaction was carried out on a 0.2 mmol scale: 1a (0.2 mmol), and 4 Å MS (100 mg) in 1.0 mL solvent, was added a solution the catalyst in 1.0 mL of the same solvent via syringe pump in 40 min under inert atmosphere.
bIsolated yields.
cDetermined by chiral HPLC analysis, see SI for details.
dThe reaction was conducted at 0 °C for 24 h.
