Figure 1.
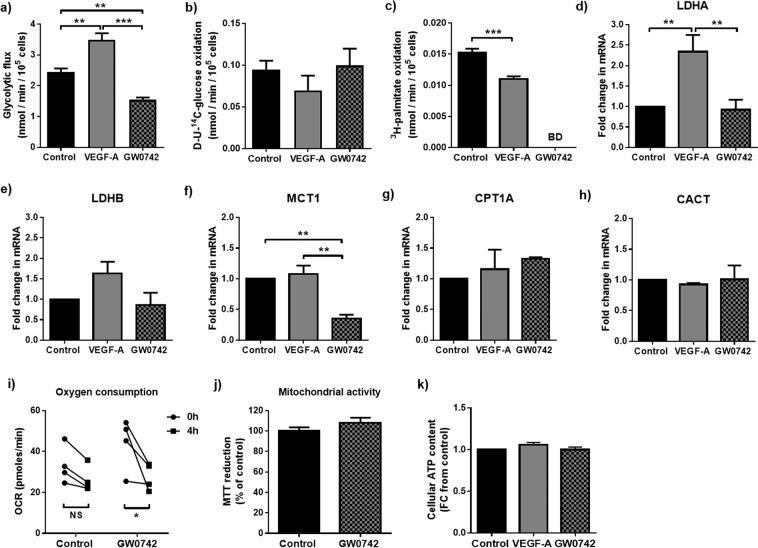
GW0742 reduces flux through central metabolic pathways whilst VEGF-A leads to metabolic activation in HUVEC monolayers. (a) GW0742 (100 nM; 4 h) significantly reduced, whilst VEGF-A (25 ng/ml; 4 h) significantly increased, glycolytic flux. (b) No change in D-U-14C-glucose oxidation rate was detected with either treatment. (c) Both VEGF-A (25 ng/ml; 5 h) and GW0742 (100 nM; 5 h) treatment reduced FAO. Data represent means (±S.E.M) of n = 3 to 5 **p < 0.01 ***p < 0.001 BD = Below level of detection; as determined by one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s post-comparison test. (d - h) RT-qPCR showing changes in LDHA, LDHB, MCT1, CPT1A and CACT mRNA expression in HUVEC monolayers treated with VEGF-A (25 ng/ml; 4 h) or GW0742 (100 nM; 4 h). Data represent means (±S.E.M) of n = 3 to 5 **p < 0.01 as determined by one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s post-comparison test. (i) GW0742 (100 nM; 4 h) significantly reduces OCR. Data represent means (±S.E.M) of n = 4 *p < 0.05 as determined by two-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni’s post-comparison test. Data were collected from 2 independent EC isolates across 2 repeats (j) GW0742 (100 nM; 4 h) has no effect on mitochondrial reducing potential. Data are means (±S.E.M) of n = 3. (k) Relative cellular ATP remains unchanged in HUVEC monolayers following treatment with VEGF-A (25 ng/ml; 4 h) or GW0742 (100 nM; 4 h). Data are means (±S.E.M) of n = 3.