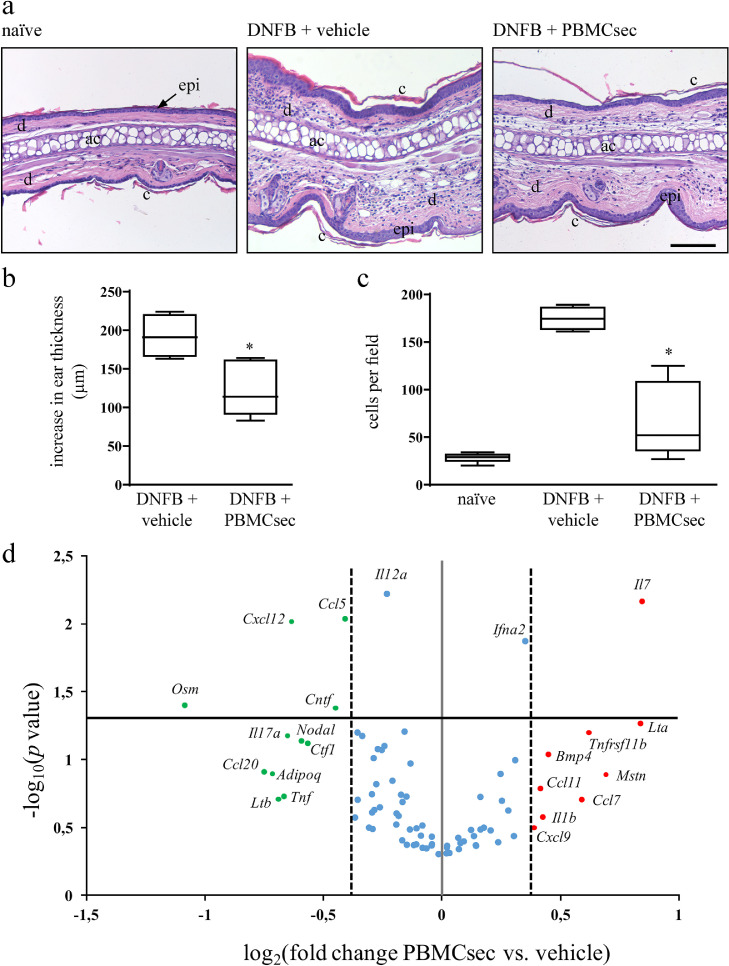
Fig. 1.
PBMC secretome alleviates ear swelling in DNFB-induced CH and abolishes immune cell recruitment to challenged skin. (a) Hematoxylin/eosin-stained ears 24 h after DNFB re-challenge with vehicle or PBMCsec treatment. Naïve ears served as untreated controls. Representative micrographs of n = 5 mice per treatment condition are shown. ac, auricular cartilage; c, cornified epidermis; d, dermis; epi, epidermis. Scale bar, 200 µm. (b) Increase in ear thickness assessed by micrometer-assisted measurements 24 h post DNFB elicitation. * indicates p<.05 PBMCsec versus vehicle. N = 5 mice per group. Ordinary one-way ANOVA was performed. Dunnett's multiple comparison test was carried out to compare groups versus vehicle control. (c) Number of cells per field. * denotes p<.05 PBMCsec versus vehicle. N = 5 mice per group. Ordinary one-way ANOVA was performed. Dunnett's multiple comparison test was carried out to compare groups versus vehicle control. (d) qPCR analysis of genes encoding cytokines and chemokines in ears of DNFB-sensitized mice. Red and green dots indicate up- and down-regulated genes, respectively, in PBMCsec- versus medium-treated ears. Blue dots represent genes considered not differentially regulated. Dotted lines denote log2-transformed 1.3-fold regulations when comparing PBMCsec and medium. Solid gray line represents log2 transformation of PBMCsec / medium = 1. Solid black line indicates -log10 of p = .05. N = 5 mice per condition. p-values were calculated by one-tailed student's t-test with equal variances between the two samples.