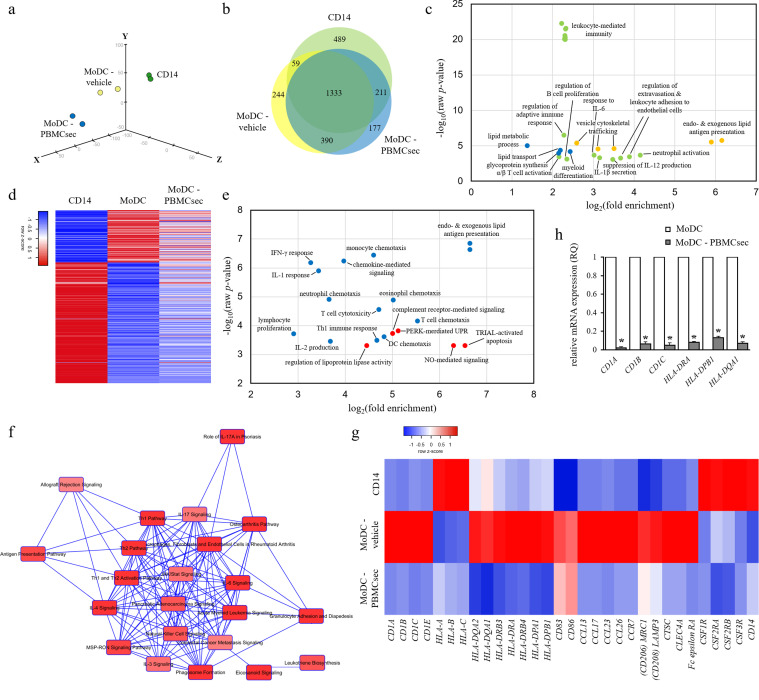
Fig. 4.
PBMCsec profoundly alters transcriptional profile of MoDC. (a) PCA of CD14+ cells and MoDCs differentiated in the presence of vehicle medium or PBMCsec. N = 2 donors per condition. (b) Genes commonly and exclusively expressed by CD14+ cells, MoDC-vehicle, and MoDC-PBMCsec are shown. Numbers indicate number of genes expressed in the respective sets. (c) GO terms associated with genes exclusively expressed in CD14+ cells (green), MoDC (yellow), and MoDC- PBMCsec (blue), respectively. Each dot represents one biological process. p-values and fold enrichments were used to depict GO terms and were calculated by PANTHER classification system. N = 2 donors per condition. (d) Genes expressed in CD14+ but not in MoDC and vice versa were compared to their expression in MoDC-PBMCsec. Z-scores were calculated by heatmapper.ca. N = 2 donors per condition. (e) GO terms of genes expressed in MoDC but not in MoDC-PBMCsec (blue) and vice versa (red). Each dot represents one biological process. Cut-off values of MoDC / MoDC-PBMCsec fold changes were set to 0.25 and 4, respectively, to identify differentially regulated genes between groups. p-values and fold enrichments were calculated by PANTHER classification system and used for visualization of the results. N = 2 donors per condition. (f) Canonical pathways activated in MoDC-vehicle but not in MoDC-PBMCsec were identified by IPA. Pathways (nodes) are connected by common genes. N = 2 donors per group. (g) Expression levels of genes related to DC function. Z-scores were calculated by heatmapper.ca. N = 2 donors per condition. (h) qPCR analysis of CD1A, CD1B, CD1C, HLA-DRA, HLA-DPB1, and HLA-DQA1 expressions in MoDC-vehicle and MoDC-PBMCsec. N = 3 donors per group. p-values were calculated by one-tailed student's t-test with equal variances between the two samples. Asterisks denote significant difference between MoDC and MoDC-PBMCsec.