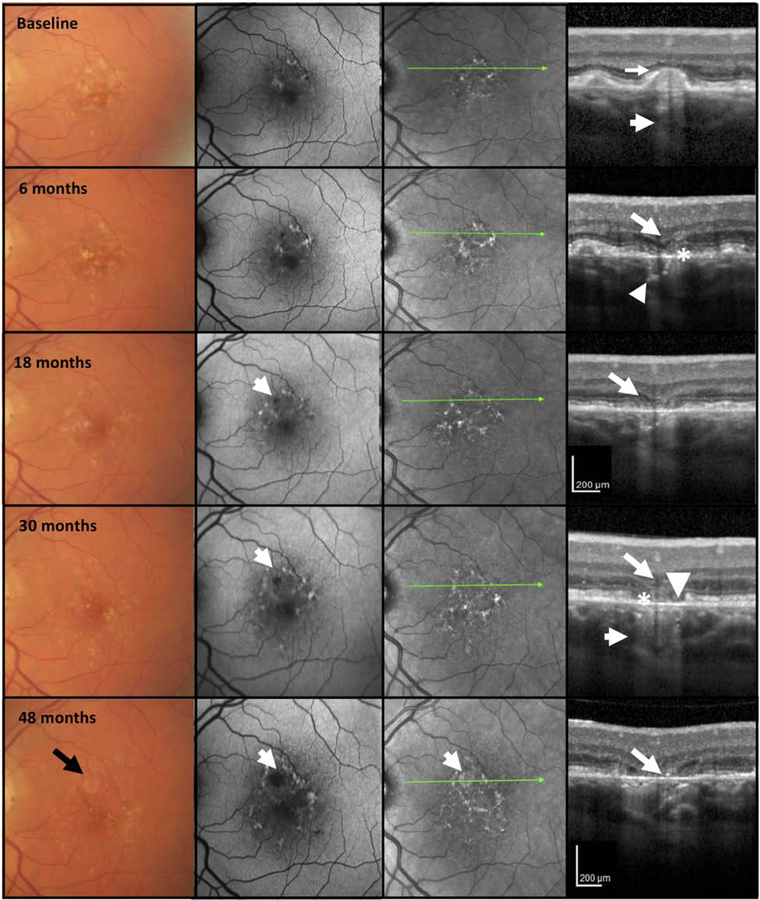
Figure 3. Multimodal imaging of an AMD case illustrating progression from incomplete to complete retinal pigment epithelium and outer retinal atrophy (iRORA and cRORA) over 48 months.
First column = color fundus photograph (CFP), second column = fundus autofluorescence (FAF), third column = near infrared reflectance (NIR), fourth column = optical coherence tomography (OCT) B-scan.
CFP of the left macula in a case illustrating large drusen and hyperpigmentation at baseline. FAF shows areas of hypo and hyper autofluorescence on FAF. The OCT at baseline shows a large druse, demonstrating hypertransmission into the choroid (small arrow). The external limiting membrane (ELM) is not clearly seen on top of this druse (large arrow) and the RPE appears intact. As such, the criteria for iRORA are not present. At 6 months, there is little change in CFP, FAF, and NIR, but on OCT, iRORA has developed, with subsidence of the inner nuclear (INL) and outer plexiform (OPL) layers (large arrow), thinning of the outer nuclear layer (ONL) and subsidence of the ELM which is still continuous. The ellipsoid zone (EZ) and RPE are discontinuous (*) and there is increased hypertransmission into the choroid (small arrow). At 18 months, whilst there is little change on the CFP, there is now a hypoautofluorescent area apparent on the FAF (small arrow). On OCT, there is a definite descent and disruption of the ELM on either side of the atrophic area, and in the midst of the atrophic area, OPL and INL subsidence (large arrow), further disruption of RPE, and possible BLamD remaining on Bruch’s membrane (BrM). At 30 months cRORA and atrophy on the FAF are evident, whilst the CFP does not demonstrate GA. The OCT has evidence of photoreceptor loss (subsidence of the INL and OPL, thinning of the ONL, discontinuous ELM descending on both sides of the atrophic area, discontinuity of the EZ and interdigitation zone (IZ) (large arrow), an area of complete RPE disruption (*) without residual BLamD > 250 μm in width and showing a bare BrM (arrowhead) and hypertransmission > 250 μm (small arrow). At 48 months, GA is identified on CFP (black arrow), enlarged area of atrophy on FAF is apparent, and atrophy is noted on the NIR image (white arrow). On OCT, the subsiding OPL within the atrophic area approaches BrM (large arrow).