Figure 1. Protease‐resistant streptavidin beads produce dramatically lower streptavidin contaminations in MS compared with regular beads.
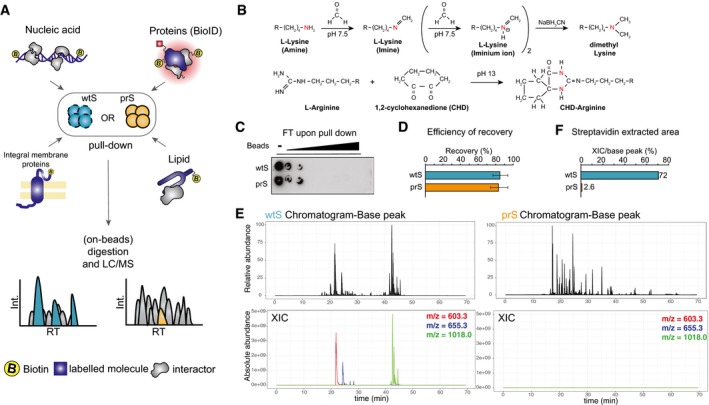
- Experimental design to target different biotinylated molecules (nucleic acids, proteins labeled by BioID, integral membrane proteins, or lipid‐interacting proteins) using either wild‐type (wtS) or protease‐resistant (prS) streptavidin beads to identify interacting proteins by MS.
- prS beads were produced by chemical modification of lysines and arginines using dimethylation condensation, respectively.
- Biotinylated DNA subjected to enrichment with increasing amount of either wtS or prS beads. Flow‐through (FT) of the pull‐down is probed with anti‐biotin antibody.
- qPCR result shows the efficiency of recovering labeled DNA using either wtS or prS beads. The error bars indicate standard deviations of two replicates.
- Base peak chromatograms in ChIP‐SICAP experiment using wtS (left) or prS (right) beads. Relative abundance is reported on the y‐axis. The absolute abundance of the top‐3 streptavidin peptides is shown using red (m/z = 603.3), blue (m/z = 655.3) and green (m/z = 1018.0).
- Relative contribution of streptavidin peaks to all base‐peaks shown in (E) using either wtS or prS beads.
