Figure 1.
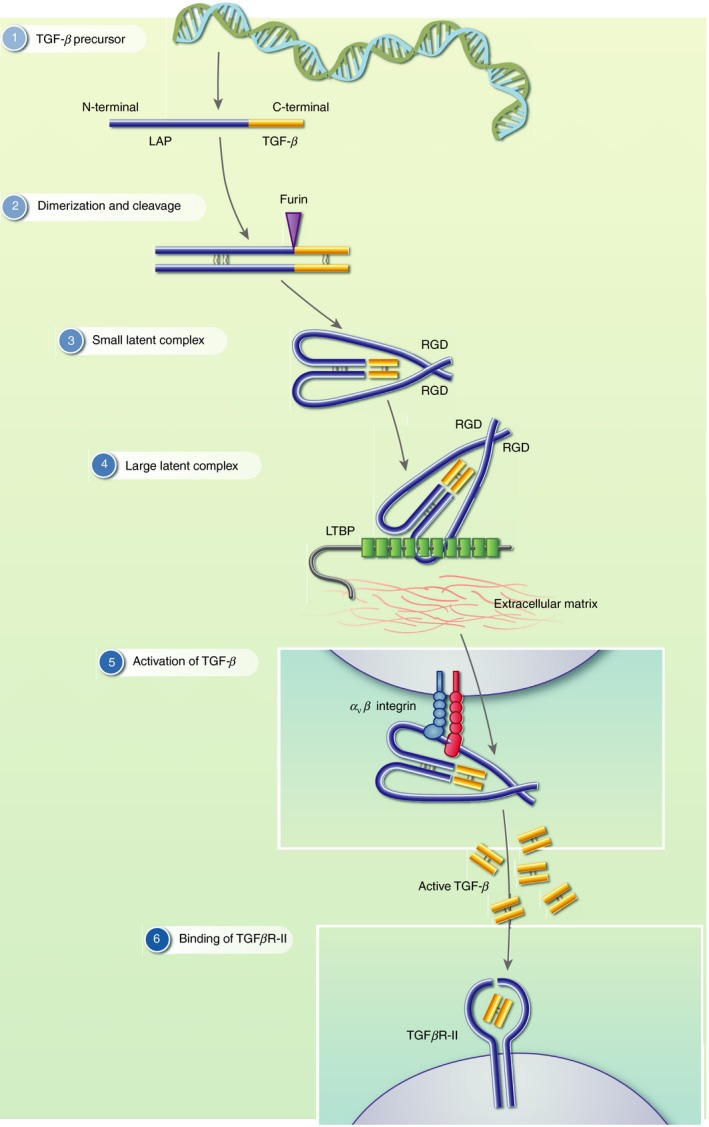
Structure of latent transforming growth factor‐β (TGF‐β) and activation by integrins. (1) TGF‐β is synthesized as a precursor that comprises an N‐terminal latency‐associated peptide (LAP) and a C‐terminal active TGF‐β moiety. (2) LAP–TGF‐β forms a homodimeric propeptide complex, which is cleaved by the protease furin intracellularly. (3) The small latent complex (SLC) comprises the cleaved LAP non‐covalently bound to active TGF‐β upon secretion. (4) Often, the SLC covalently associates with latent TGF‐β binding protein (LTBP) to form the large latent complex (LLC) together with the extracellular matrix. (5) α v integrins important activators of TGF‐β binds to LAP at an arginine‐glycine‐aspartic acid (RGD) site, leading to the dissociation of LAP and the release of active TGF‐β. (6) Active TGF‐β first binds to the TGFβRII dimer.
