Figure 2.
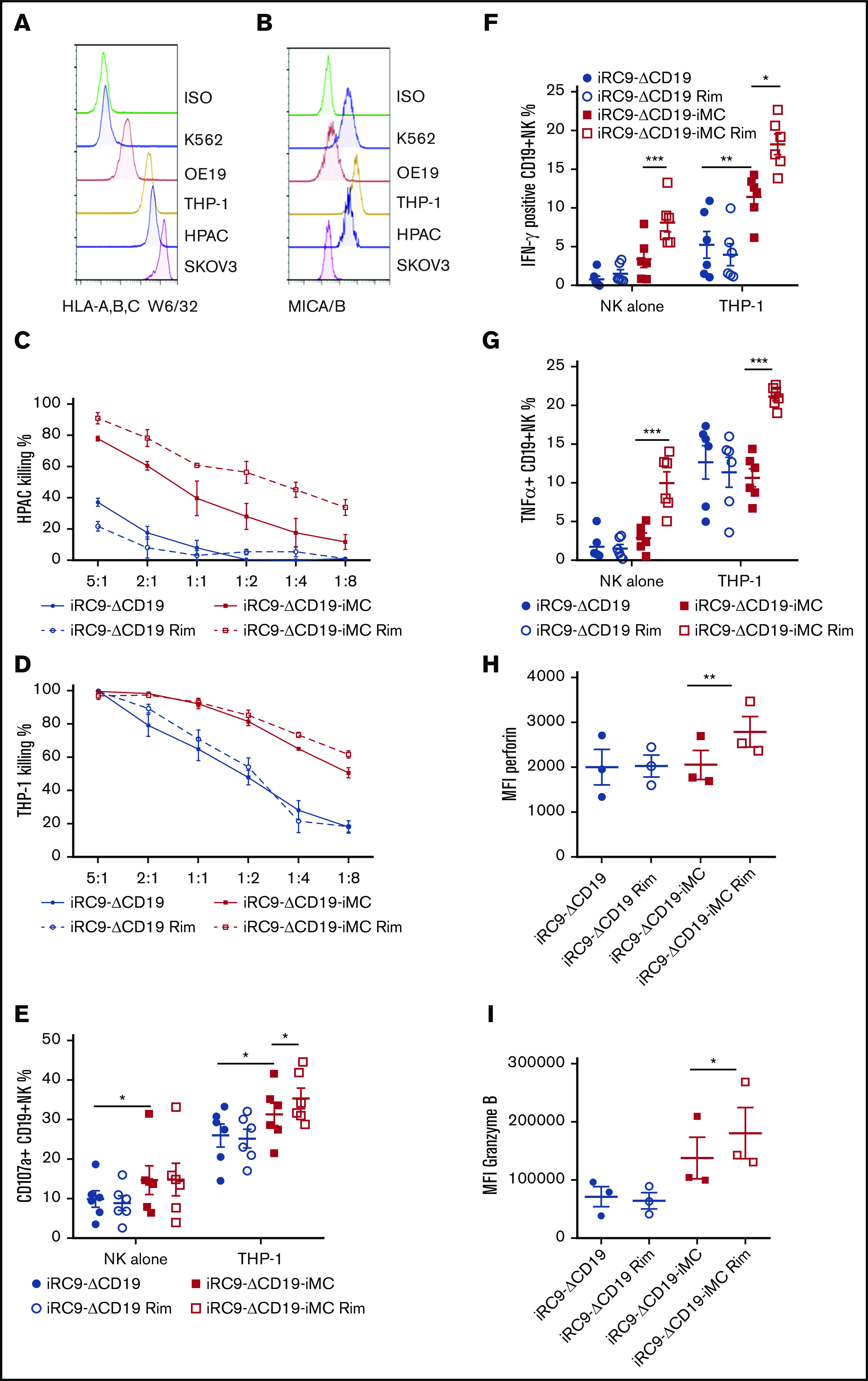
iMC enhances NK cell targeting of tumor cells. (A-B) Flow cytometric analysis to assess MHC class 1 surface expression of tumor cell lines using anti–HLA-A,B,C antibody (clone w6/32) and surface expression of the NKG2D ligands using MICA/B-specific antibody. (C-D) Potency of NK cells modified with iRC9-iMC or iRC9 was tested in 24-hour coculture assays with HPAC-eGFPFfluc or THP-1–eGFPFfluc at decreasing effector/target ratios. Tumor cell killing percentages were calculated by luciferase activity relative to tumor cells alone; 2-way analysis of variance statistical analysis (n = 4; P < .0001). (E-I) iRC9- or iRC9-iMC–modified NKs were incubated with or without THP-1 targets for 4 hours (E) or overnight (F-I) in the presence or absence of 1 nM of rimiducid (Rim). Percentages of cells expressing surface CD107a (E), intracellular interferon-γ (IFN-γ) (F), and tumor necrosis factor α (TNF-α) (G) were measured by flow cytometry. Mean fluorescence intensities (MFIs) of perforin (H) and granzyme B (I) were measured in NK cells cocultured with THP-1 overnight. Transduced NK cells were first gated as CD56+CD19+ population. Paired Student t test was used to compare indicated groups. *P < .05, **P < .01, ***P < .001.
