Fig 5.
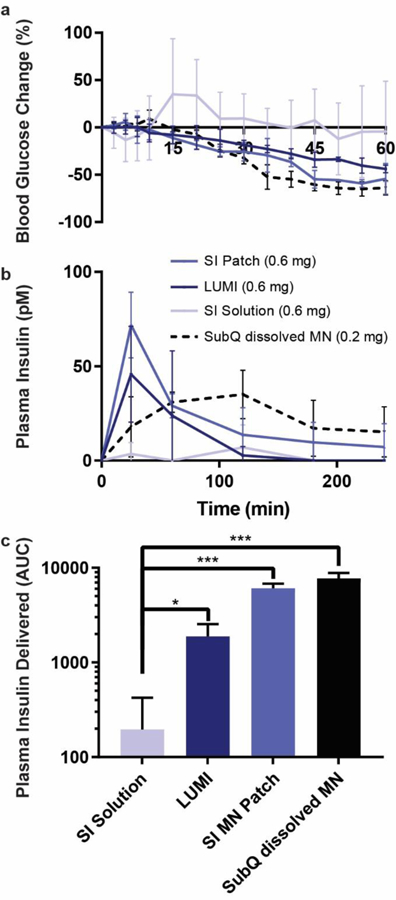
In vivo insulin delivery via LUMI in swine. (a) Blood glucose and (b) plasma insulin levels are determined. Two LUMI devices were deployed in each swine jejunum and delivered a total of 0.6 mg of insulin in polyvinylpyrrolidone microneedle patches. Delivery was compared to an equivalent insulin dose from a microneedle patch dissolved in 10 mL water delivered to the lumen of the jejunum (SI Solution), a microneedle patch applied directly to the jejunum (SI MN Patch), or a microneedle patch dissolved in 0.5 mL of sterile saline, filtered and subcutaneously injected (SubQ dissolved MN) (n=3). After filtration some insulin was lost, and the subcutaneous insulin dose was calculated to be 0.2 mg. (c) The total plasma insulin (calculated using the area under the curve, AUC) delivered by each method after extrapolating the data out to infinite time. (Error Bars=SD; *P<0.05, ***P<0.001).
