Figure 1.
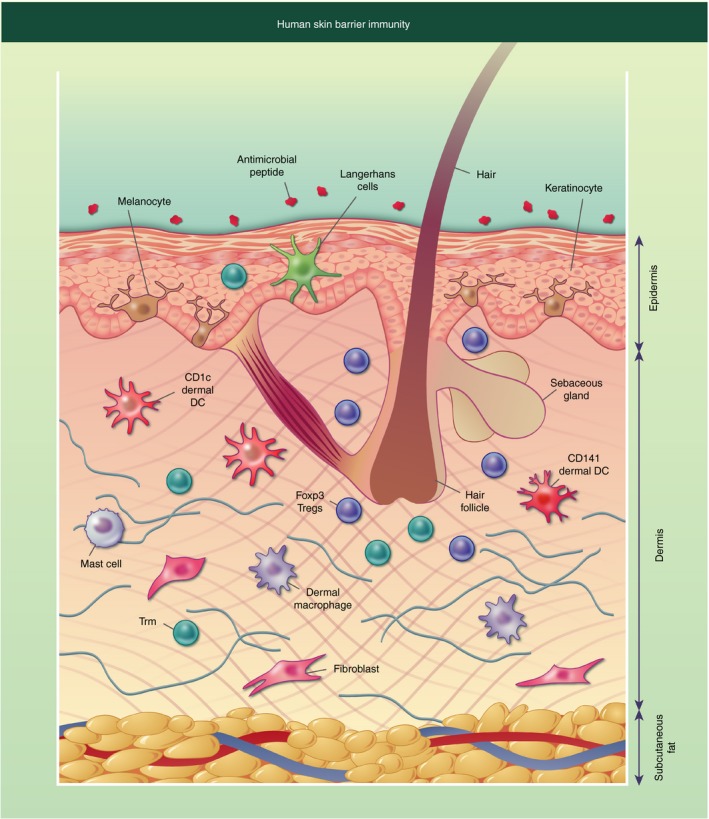
Diagrammatic representation of human skin barrier immunity. The surface of the skin is covered in antimicrobial peptides and lipids, some of which originate from the sebaceous gland located near the hair follicle. The epidermis consists of keratinocytes forming stratified corneum, with melanocytes interspersed. Langerhans cells and T resident memory cells (Trm) can also be found in the epidermis. The dermis has a more diverse collection of cells including structural cells such as fibroblasts, and immune cells such as dermal dendritic cells (DCs) and macrophages, CD4+ and CD8+ Trm, mast cells and Foxp3+ T regulatory cells (Tregs), which are often located near the hair follicle. The final layer of the skin is the subcutaneous fat, which is primarily composed of adipocytes.
