Fig. 6. Schematic representation of the major stages of lipid redox metabolism leading to the formation of HOO-AA-PE as a pro-ferroptotic signal.
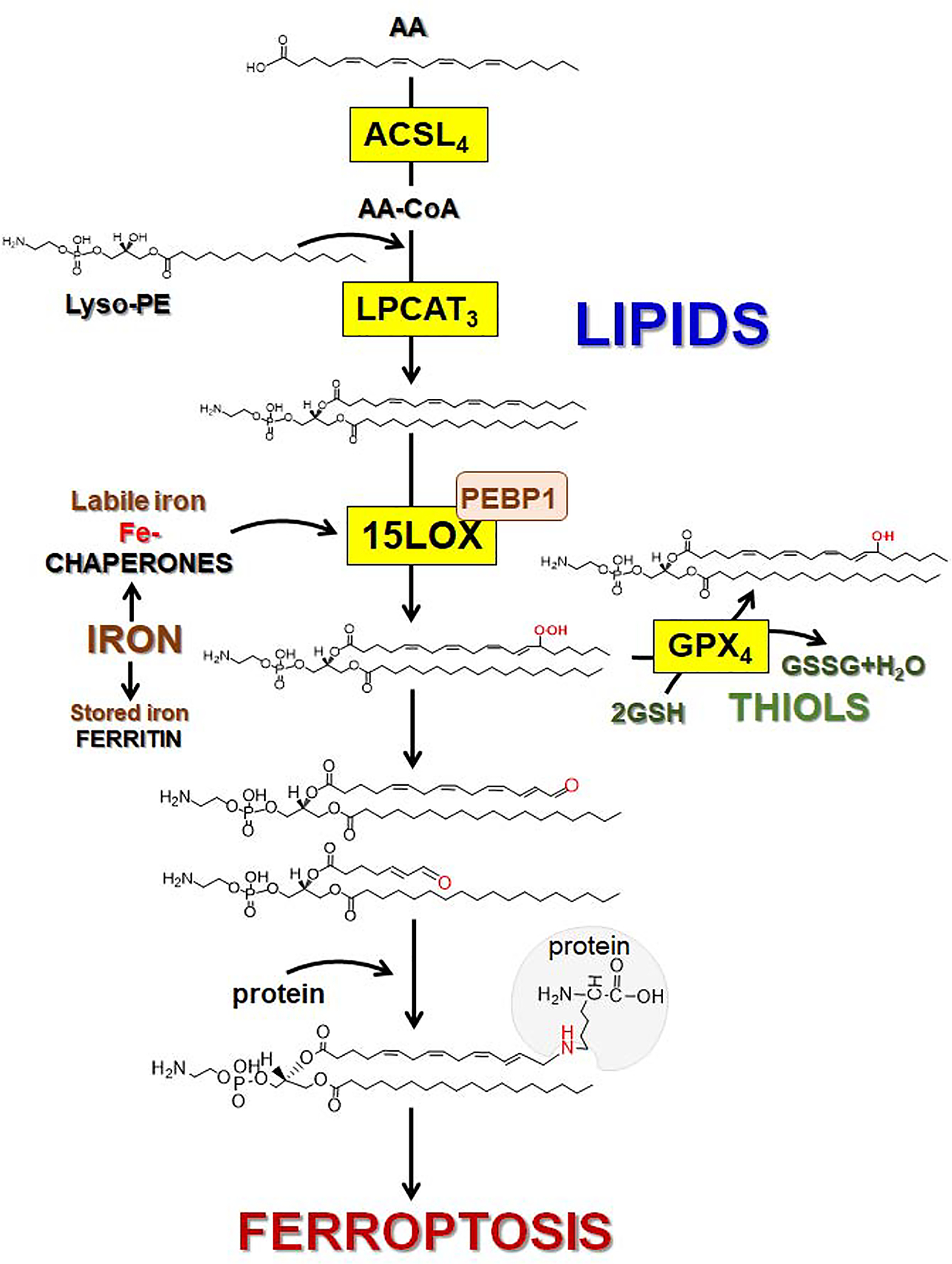
Esterification of arachidonic acid (AA) into phosphataidylethanolamine (PE) requires acyl-CoA synthase 4 (ACSL4) catalyzed formation of AA-CoA which is used for the AA esterification into lyso-PE driven by lysophosphatidyl-choline acyltransferase 3 (LPCAT3) to yield AA-PE. Assembly and engagement of 15-LOX/PEBP1 enzymatic complexes changes 15-LOX substrate selectivity from AA to AA-PE thus facilitating the generation of specific product (15-HOO-AA-PE). Under ferroptotic conditions, the activity of GPX4 is inhibited, thus HOO-AA-PE cannot be reduced to HO-AA-PE. In contrast oxidatively-truncated electrophilic products of HOO-AA-PE with shortened side chains and electrophilic oxygen functionalities are formed. These oxidatively-truncated PE products form adducts by attacking nucleophilic sites in target proteins thus leading to the yet to be identified gateway ferroptotic complexes.
