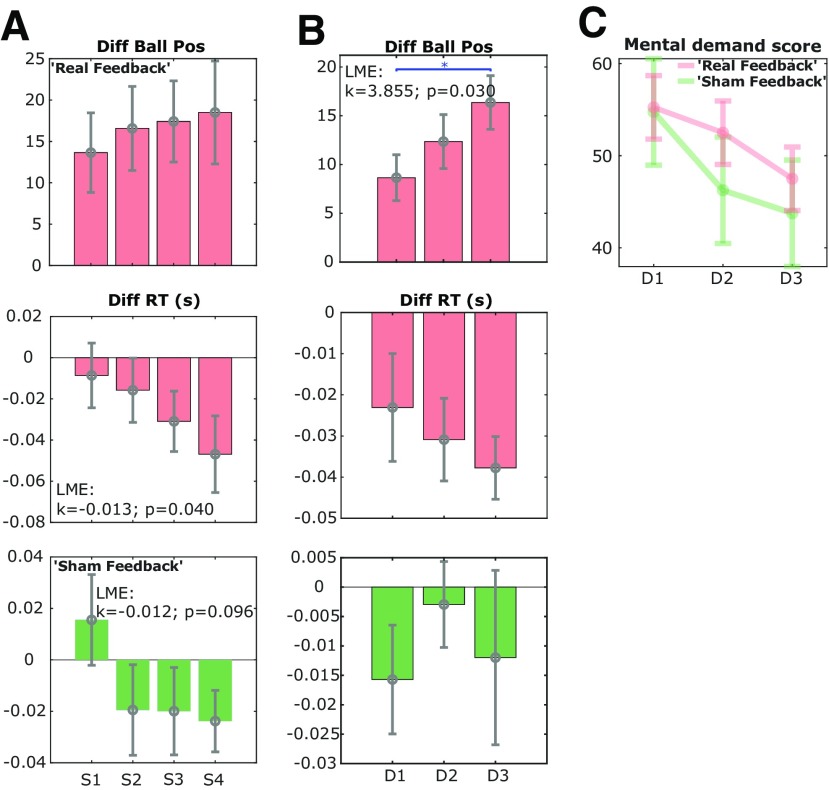
Figure 7.
The learning effect of neurofeedback training was achieved across experimental runs and across training days. A, The averaged difference in the basketball position (upper) and the RT (middle) between training and no training conditions across four experimental runs (S1–S4) on the first training day for all hemispheres in the real feedback group, and the difference in the RT for the sham feedback group (bottom). B, The averaged difference in the basketball position (upper) and the RT (middle) between training and no training conditions across three training days (D1–D3) for those 75% hemispheres with the worst training effect on the first day in the real feedback group. The bottom subplot column indicates the averaged difference in RT between training and no training conditions for the 75% hemispheres with the worst training effect on the first day in the sham feedback group. C, Self-reported mental demand scores decreased over the training days in both real feedback and sham feedback groups, but no significant difference was observed between these two groups. *p < 0.05.