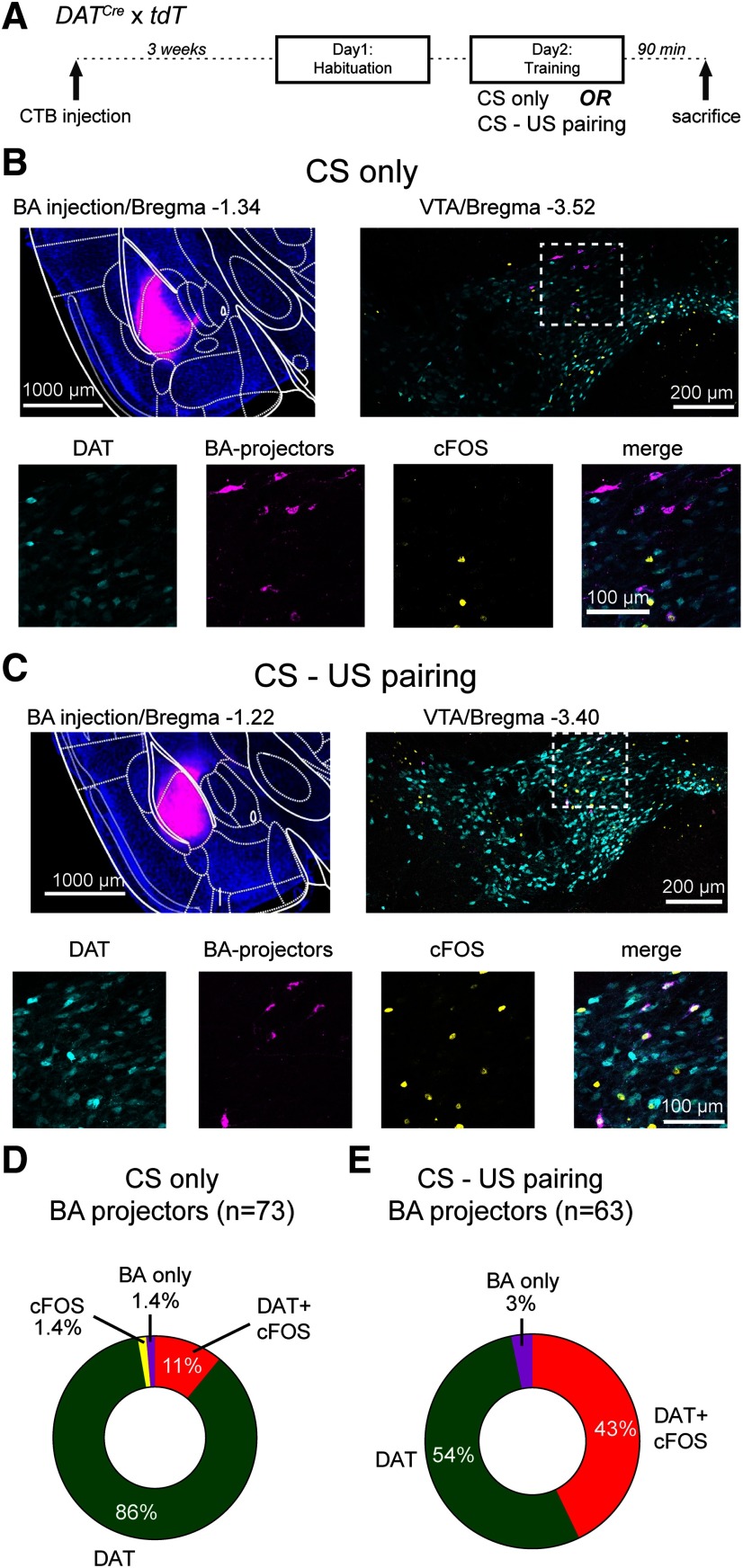
Figure 3.
Combined cfos labeling and retrograde tracing show that BA projectors increase their activity during tone-footshock pairing. A, Schematic of the protocol used for cfos labeling; 90 min after the training session, mice were killed and prepared for cfos immunohistochemistry. B, Example images from a mouse that received only tones during the training on day 2 (CS only; control group). Top left, Wide-field fluorescence image of the BA injected with CTB-Alexa-647 for retrograde labeling (magenta channel). Top right, Confocal image on the level of the VTA, with tdTomato-positive DAT+ neurons (cyan channel) as well as labeling by the cfos antibody (yellow channel) and by CTB-Alexa-647 (magenta). Bottom row, Images represent the individual and merged channels for the boxed area in the top right. C, Corresponding images from a different mouse, which underwent CS-US pairing (i.e., with footshocks) during the training day. D, Quantification of all CTB-labeled neurons (BA projectors; n = 73) and their colabeling in N = 2 mice in the control group. A large percentage of BA projectors is DAT+ (the sum of DAT and DAT+ cfos classes; 97%), but only 11% are stained by cfos. E, Quantification of all CTB-labeled neurons (BA projectors; n = 63) from N = 2 mice that underwent the CS-US pairing before cfos immunohistochemistry. Note the larger percentage of DAT+, cfos+ BA projectors (43%; for statistical analysis, see Results).