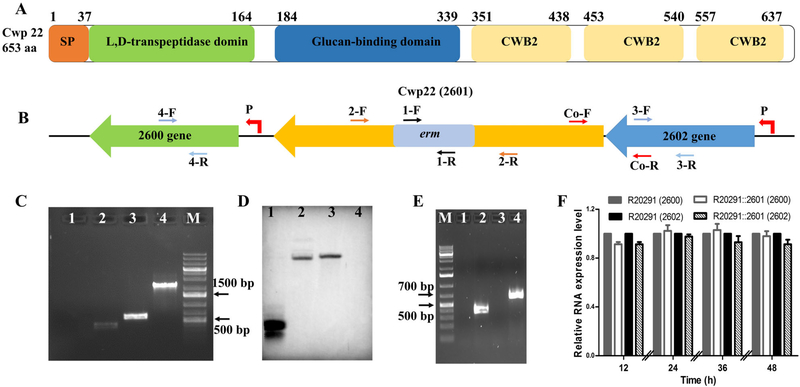
Fig. 1.
Construction and identification of cwp22 mutant.
A. Schematic representation of Cwp22 structure. Cwp22 contains a 37 amino acid signal peptide, and three main domains that are N-terminal catalytic domain, C-terminal three repeats cell wall binding motif CWB2 (pfam04122) and 8 type 1 cell wall binding (CWB1- glucan binding domain) repeats.
B. Up and down stream genes of 2601 (cwp22). P indicates promoter.
C. Identification of cwp22 mutation. M: 1 kb DNA ladder; 1: ermB gene verification with R20291 genome using primer 1-F/R; 2: ermB gene verify-cation with R20291::2601 genome using primer 1-F/R; 3: correct insertion verification with R20291 genome using primer 2-F/R; 4: correct insertion verification with R20291::2601 genome using primer 2-F/R.
D. Verification of single insertion mutation by Southern blot analysis. 1: ermB gene used as a positive control; 2: R20291::2601 genome digested with EcoRI and XbaI; 3: R20291::2601 genome digested with EcoRI and Hind III; 4: R20291 genome digested with EcoRI and Hind III used as a negative control.
E. Verification of 2601 truncation and co-transcription of 2601 and 2602 genes. 1: Test of genomic contamination in total R20291 RNA using 16 s primers; 2: Test of 2601 and 2602 co-transcription with R20291 cDNA as template using primer Co-F/R; 3: Test of 2601 gene transcription with R20291::2601 cDNA as template using primer 2-F/R; 4: Test of 2601 gene transcription with R20291 cDNA as template using primer 2-F/R.
F. Test of polar effect of 2601 gene inactivation on up and down stream genes. Primers 2-F/R, 3-F/R and 4-F/R were used to detect the transcription of 2601, 2602 and 2600 genes respectively. Experiments were independently repeated thrice. Bars stand for mean ± SEM. One-way ANOVA was used for statistical significance.