Figure 6. Neat1-knockdown improves long-term memory in aged animals.
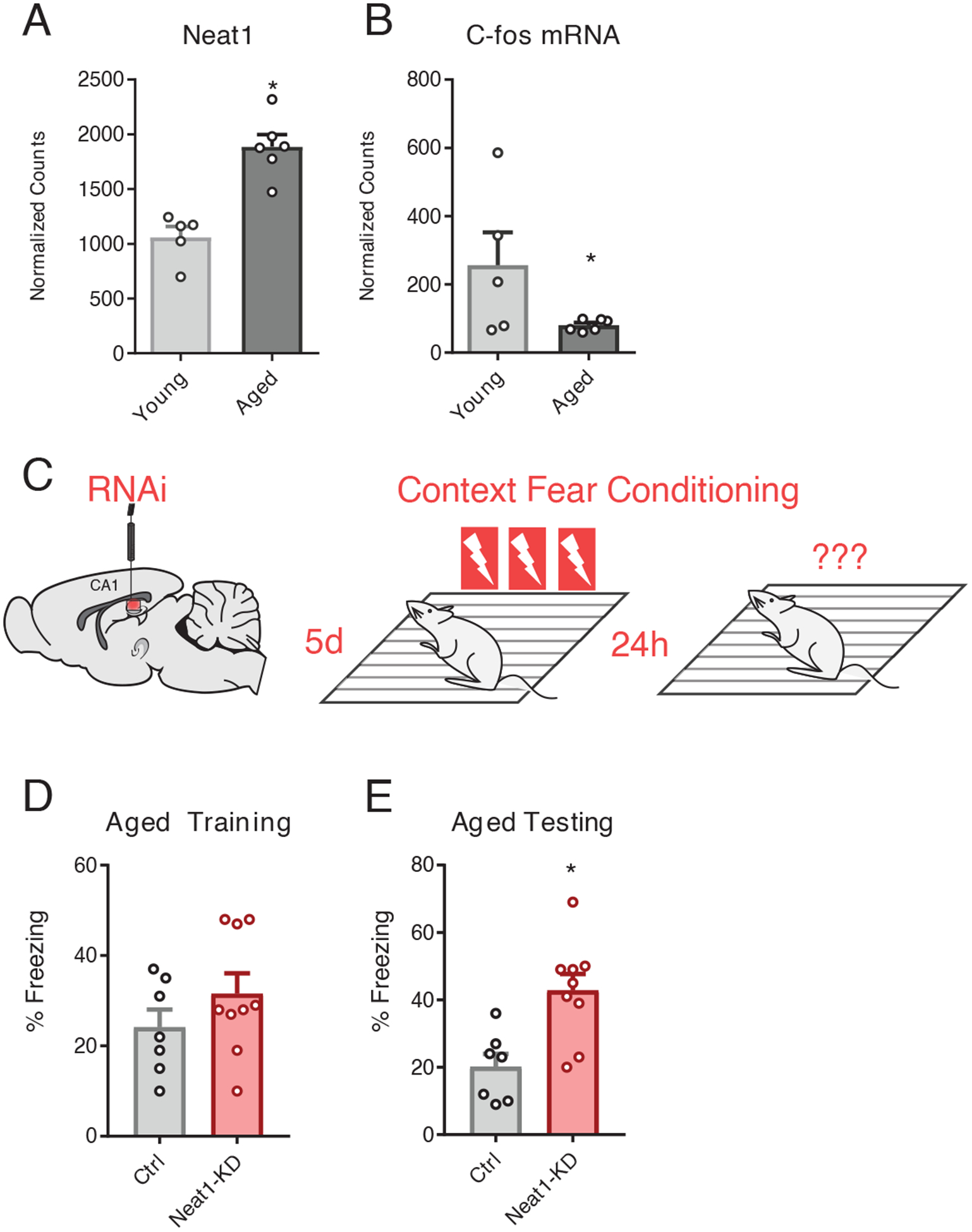
(A and B) DESeq2-generated normalized counts for Neat1 (A) and c-Fos (B) from RNAseq assay of hippocampi from 3mo and 24mo C57/B6 mice. Data are means ± SEM from n = 5 to 6 mice, *Benjamini-Hochberg (BH) adjusted p < 0.05. Neat1 abundance (A) and c-Fos mRNA abundance were (*BH corrected p < 0.05) (B) was significantly repressed in aged hippocampi relative to the hippocampi of young mice. (*BH corrected p < 0.05) (C) Graphic depiction of siRNA infusion into hippocampal area CA1 and three shock-pairing contextual fear conditioning paradigm. Briefly, 18mo old male C57/B6 mice were trained 5 days after bilateral infusion of siRNAs and tested 24 hours after training. (D) Freezing behavior of mice described in (C) as a percent of time during the training phase of the contextual fear conditioning paradigm. No significant difference detected; data are means ± SEM from n = 7 to 9 mice, assessed by Student’s t-test. (E) Freezing behavior of mice described in (C) as a percent of time during the testing phase of the contextual fear conditioning paradigm. Data are means ± SEM from n = 7 to 9 mice, *p = 0.0039 by Student’s t-test.
