Figure 1:
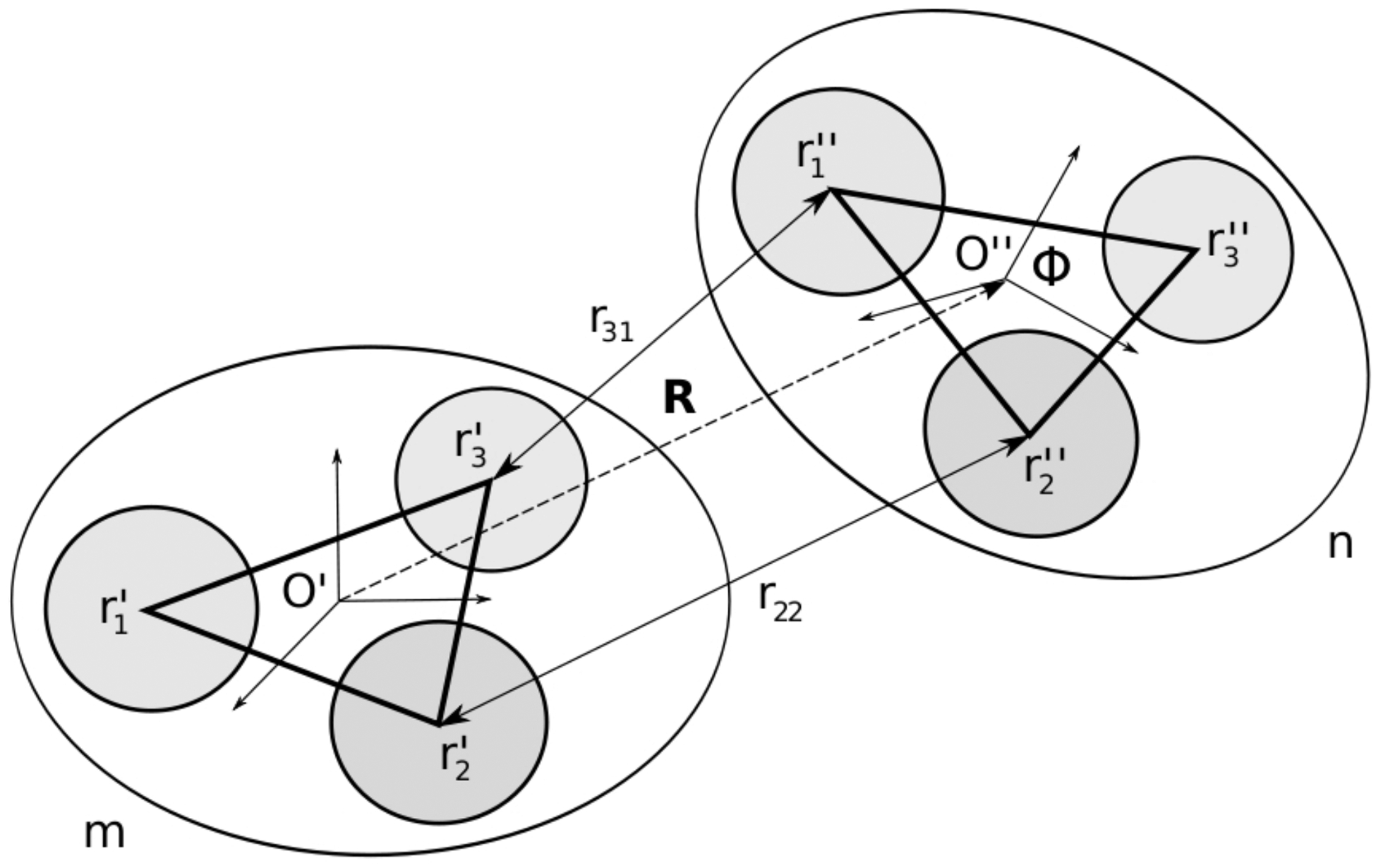
Geometry of two rigid bodies m and n with Mm = 3 and Mn = 3 interaction centers, respectively. Local coordinate frames O′ and O″ are assigned to the rigid bodies. The positions of the interaction centers in the local coordinate frames are denoted by r′ and r″ vectors. The position of the O″ origin in the O′ coordinate frame is defined by the translation vector R. The rotation, which transforms the O″ frame into the O′ frame is defined by the Euler angles Φ. The distances between the centers of interaction are given by the equation (5).
