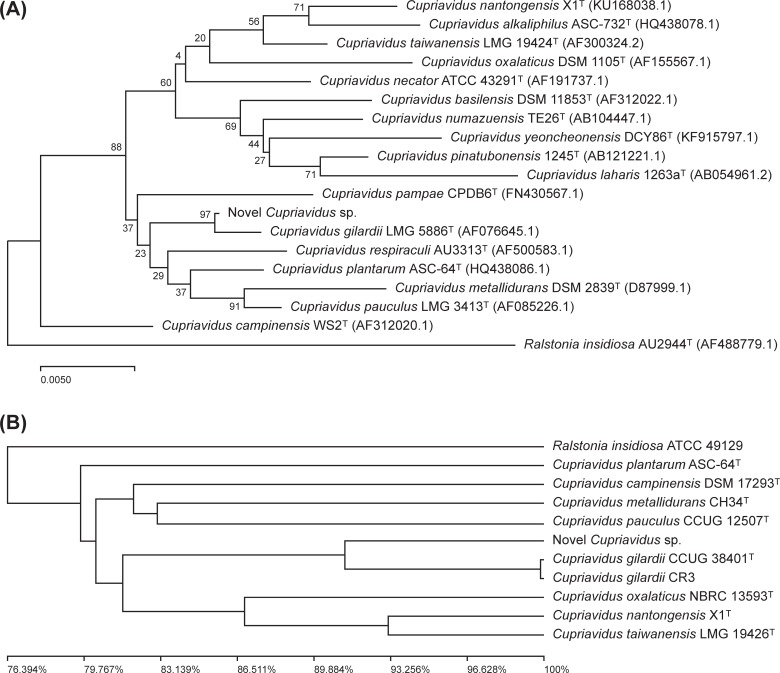
Fig 1. Phylogenetic tree based on 16S rRNA gene sequencing and whole genome sequencing in the relationships of novel Cupriavidus species and the other species of the genera Cupriavidus and Ralstonia.
A) Neighbor-joining phylogenetic trees based on 16S rRNA gene sequences using Ralstonia insidiosa as an outgroup. The percentage of replicated trees in which the associated taxa clustered together in the bootstrap test (1000 replicates) are shown next to the branches. The evolutionary distances were computed using the Jukes-Cantor method. B) The genomic phylogenetic tree generated by the unweighted pair group method with arithmetic mean clustering method and average nucleotide identity value using Ralstonia insidiosa as an outgroup. The complementary average nucleotide identity value to 1 was used to calculate the distance. The tree was drawn to scale, with branch lengths in the same units as those of the evolutionary distances used to infer the phylogenetic tree.