Fig. 6. Robust formation of mouse-human chimeric embryos.
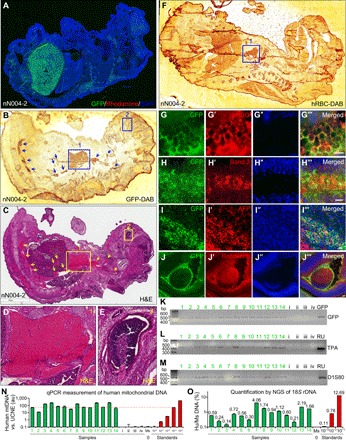
(A) Large amounts of GFP+ human cells were found in an E17.5 mouse embryo (nN004-2) derived from mouse blastocysts injected with GFP-labeled naïve N004 iPSCs (injection #6). (B to E) At a different z-level from (A), two neighboring sections of this embryo were DAB stained with anti-GFP (B) or stained with H&E (C). Boxes 1 (heart) and 2 (retina) in (B) correspond to boxes 1 and 2 in (C), which are enlarged in (D) and (E), respectively. Areas highlighted by arrows and box 1 contained GFP+ (B) RBCs (C and D). Box 2 contained GFP+ (B) retinal pigmented epithelium (C and E). (F to J‴) Different sections of this embryo were DAB stained with antibody against hRBC (F) or immunostained for GFP (G to J), hRBC (G′; mesoderm), the RBC marker Band 3 anion transporter (H′; mesoderm), AFP (I′, endoderm), and the photoreceptor marker recoverin (J′; ectoderm). (G) to (G‴) correspond to boxed areas of fig. S4 (A to A‴). Boxed area in (J‴) is enlarged in fig. S4B. Scale bars, 10 μm. (K to M) PCR detection of GFP (K) or human-specific DNA using DNA fingerprinting primers TPA-25 (L) or D1S80 (M) in genomic DNA isolated from E17.5 mouse embryos derived from mouse blastocysts injected with GFP-labeled naïve RUES2 (embryos 1 to 14; injection #12) or unlabeled naïve RUES2 (embryos i to iv; injection #14). GFP, GFP plasmid as positive control; RU, genomic DNA from RUES2. (N) qPCR measurements of hmtDNA normalized against ultraconserved noncoding element (UCNE) in genomic DNA isolated from the above samples (1 to 14 and i to iv; green bars), C57BL/6 mouse genomic DNA (Ms) and RUES2 human genomic DNA serially diluted in C57BL/6 mouse genomic DNA (red bars). Red dotted line highlights level equivalent to 1:1000 diluted standard. (O) Quantification of human and mouse 18S rDNA by NGS of PCR amplicons of the positive samples in (N) (green bars), C57BL/6 mouse genomic DNA (Ms), and RUES2 human genomic DNA serially diluted in C57BL/6 mouse genomic DNA (red bars). Sequences of the human and mouse amplicons are identical at the primer binding sites on both ends and diverge by 9 bp in the middle of the amplicons. This enables unbiased PCR amplification of human and mouse DNA and their absolute quantification by counting human and mouse reads in NGS.
