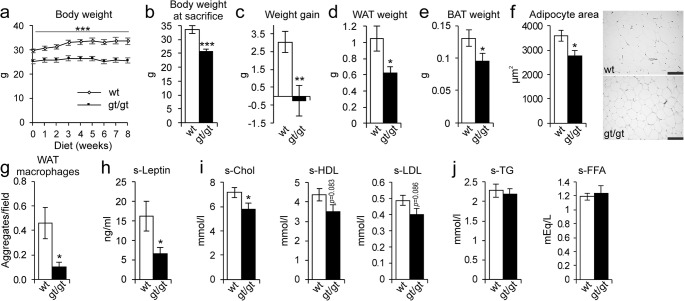
Fig. 1.
HIF-P4H-2-deficient mice are protected against high-fat, high-fructose (HFHF) diet–induced obesity, adipose tissue inflammation, and high cholesterol levels. Wild-type (wt) and Hif-p4h-2gt/gt (gt/gt) males were studied while on an 8-week HFHF diet (n = 8–10/group). a Body weight development during the diet. b Body weight at sacrifice. c Weight gain at the end of the diet relative to weights on the day before the diet started. d Weight of gonadal WAT. e Weight of BAT. f Cross-sectional area of WAT adipocytes. Scale bar = 100 μm. g Number of macrophage aggregates in WAT. h Serum leptin levels. i Serum total cholesterol, HDL cholesterol, and LDL cholesterol levels. j Serum TG and FFA levels (n = 6–10/group for FFA). Data are means ± SEM. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001. BAT, brown adipose tissue; FFA, free fatty acids; s, serum; TG, triglycerides; WAT, white adipose tissue