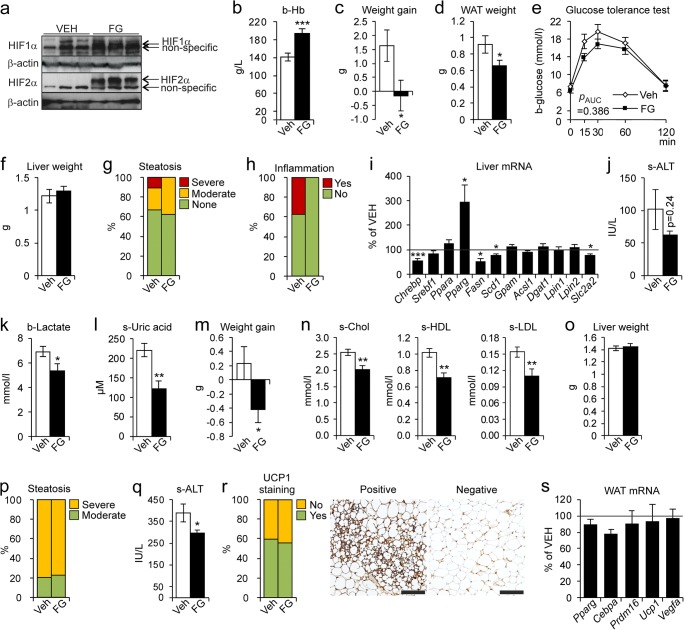
Fig. 7.
Pharmacological inhibition of HIF-P4Hs ameliorates diet-induced obesity, metabolic dysfunction, and liver damage. Wild-type (wt) females were fed a high-fat, high-fructose (HFHF) diet for e 4 or a–d, f–l 6 weeks or a high-fat, methionine-choline-deficient (HF-MCD) diet for m–s 3 weeks and simultaneously given vehicle (VEH) or 60 mg/kg of FG-4497 (FG) on days 1, 3, and 5 of each week (n = 8–10/group). a Western blot analysis of hepatic HIF1α and HIF2α protein levels. β-Actin was used as a loading control. b Blood hemoglobin levels. c Weight gain at the end of the diet relative to weights on the day before the diet started. d Weight of gonadal WAT. e Oral glucose tolerance test. The value for 0 min was determined after a 12-h fast. f Liver weight. g Scoring of hepatic steatosis. Steatosis grading: “None” corresponds to scores 0–2, “Moderate” to 3, and “Severe” to 4. h Scoring of liver inflammation. “No” corresponds to score 0 and “Yes” to 1–2. i qPCR analysis of liver mRNA levels of FG-treated mice relative to VEH-treated, studied relative to TATA-box-binding protein mRNA. j Serum ALT levels. k Blood lactate levels. l Serum uric acid levels. m Weight gain at the end of the HF-MCD diet relative to weights on the day before the diet started. n Serum total cholesterol, HDL cholesterol, and LDL cholesterol levels. o Liver weight. p Scoring of hepatic steatosis. Steatosis grading: “Moderate” corresponds to score 2 and “Severe” to 3. q Serum ALT levels. r Scoring of UCP1-stained WAT sections. “No” corresponds to < 5% of UCP1 staining/field and “Yes” to 5–25%. Images are representative of scoring for the VEH group. Scale bar = 200 μm. s qPCR analysis of WAT mRNA levels of FG-treated mice relative to VEH-treated group, studied relative to peptidylprolyl isomerase A mRNA. b–f, i–o, q, s Data are means ± SEM. *p ≤ 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001. ACSL1, acyl-CoA synthetase long-chain family member 1; ALT, alanine aminotransferase; b, blood; CEBPA, CCAAT-enhancer-binding protein alpha; CHREBP, carbohydrate-responsive element-binding protein; DGAT1, diacylglycerol o-acyltransferase 1; FASN, fatty acid synthase; GPAM, mitochondrial glycerol-3-phosphate acyltransferase; LPIN, lipin; PPAR a/g, peroxisome proliferator–activated receptor alpha/gamma; PRDM16, PR/SET domain-16; s, serum; SCD1, stearoyl-CoA desaturase 1; SLC2A2, solute carrier family-2 member 2; SREBF1c, sterol regulatory element-binding protein 1c; UCP-1, uncoupling protein 1; VEGFA, vascular endothelial growth factor A; WAT, white adipose tissue