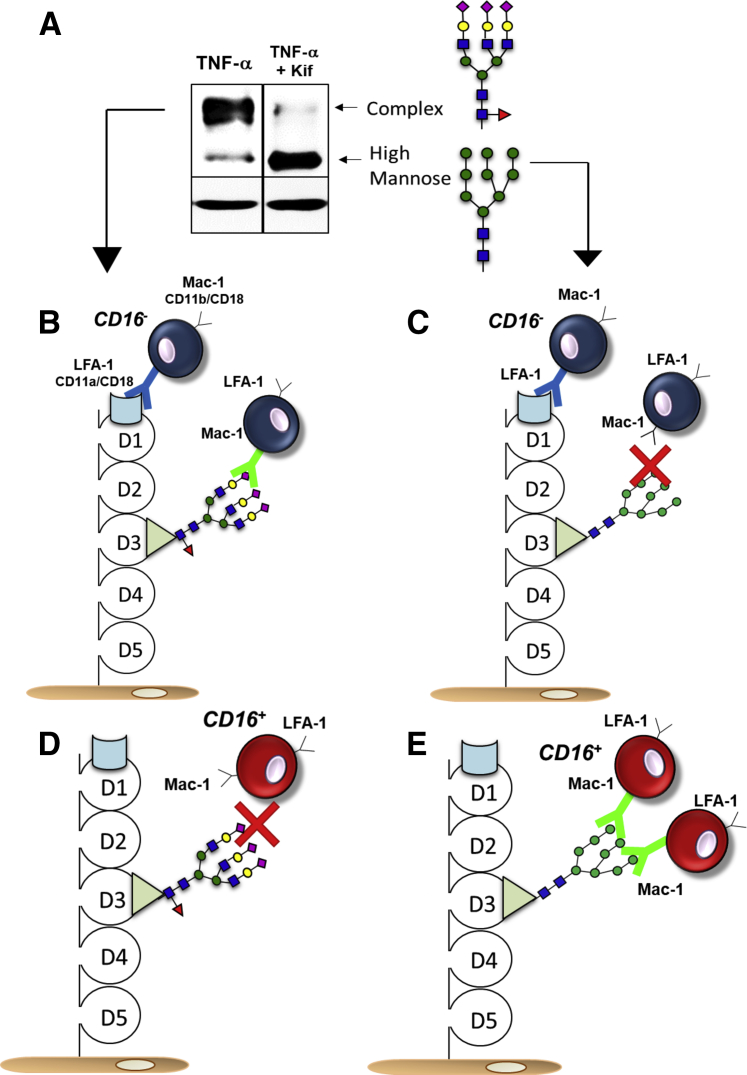
Figure 3.
A: Representative Western blot analysis of intercellular adhesion molecule 1 (ICAM-1) from tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α (10 ng/mL, 4 hours) treated human umbilical vein endothelial cells with or without kifunensine (Kif; class I α-mannosidase inhibitor) pretreatment to demonstrate high-mannose ICAM-1 formation. B: CD16− monocytes adhere to ICAM-1 via the lymphocyte function–associated antigen 1 (LFA-1) domain or macrophage-1 antigen (Mac-1) domain when the latter is modified with complex N-glycans. C: CD16− monocytes do not adhere to the Mac-1 domain when it is modified with high-mannose N-glycans. D: CD16+ monocytes adhere to neither the LFA-1 domain of ICAM-1 nor the Mac-1 domain modified by complex N-glycans. E: CD16− monocytes only bind to the Mac-1 domain when it is modified by high-mannose N-glycans.