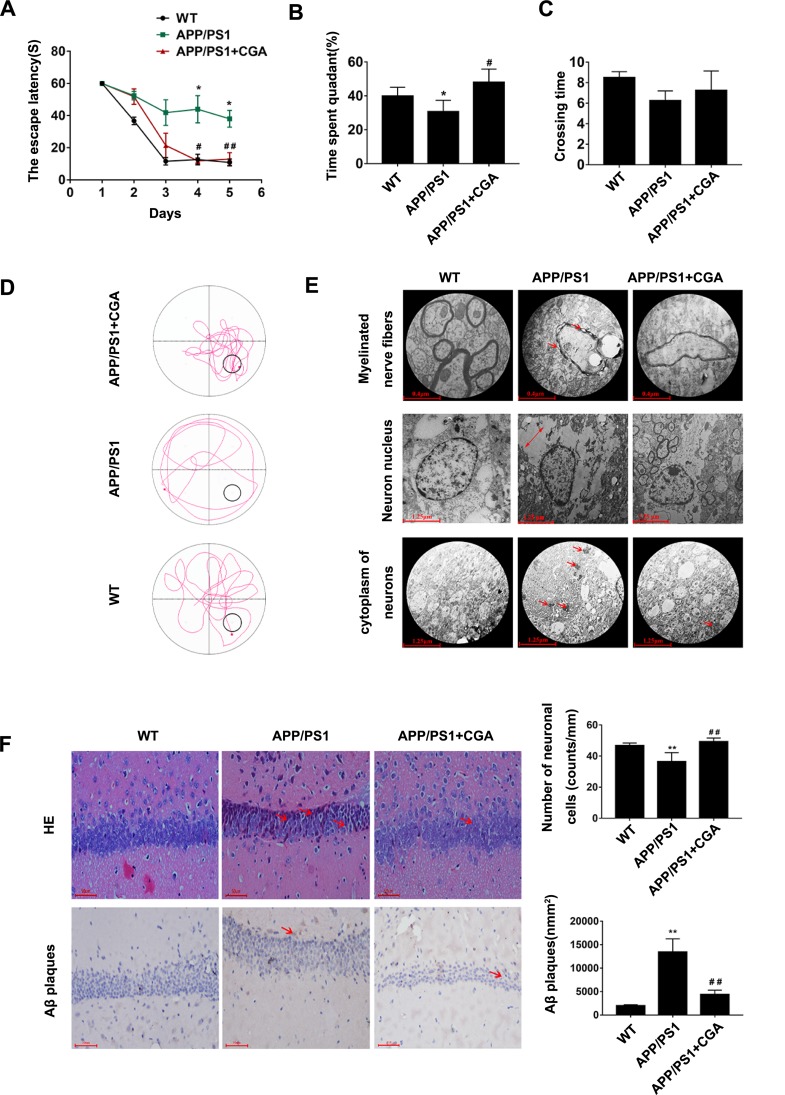
Figure 1.
CGA alleviated spatial memory impairment in APP/PS1 mice and Aβ25-35- induced neuron damage in SH-SY5Y cells.
Notes: (A) The escape latency of mice. (B) The percentage of time spent in the target quadrant. (C) The crossing times. (D) Representative swimming trajectories of the mice on the fifth trial day. (E) Electron micrograph of neurons in the hippocampal CA1 area of the mice.1) Myelinated nerve fibers (upper panel, arrowheads represent the Demyelination characteristics). 2) Neuron nucleus (middle panel, two-way arrows represent the intercellular space). 3) cytoplasm of neurons (lower panel, arrowheads represent the high electronic density materials). (F) Representative H&E stained neurons in the hippocampal CA1 area of the mice (upper panel, arrowheads represent the nuclear pyknosis), and immunohistochemical staining results of Aβ plaques (lower panel, arrowheads represent the Aβ plaques). Data are expressed the mean ± s.e.m for eight samples per treatment group. *P<0.05, **P<0.01 compared with the WT group or the no Aβ25-35-treatment group; #P<0.05, ##P<0.05 compared with the APP/PS1 group or Aβ25-35-treatment group.
Abbreviations: CGA, chlorogenic acid; AD, Alzheimer’s disease; LTR, LysoTracker Red.