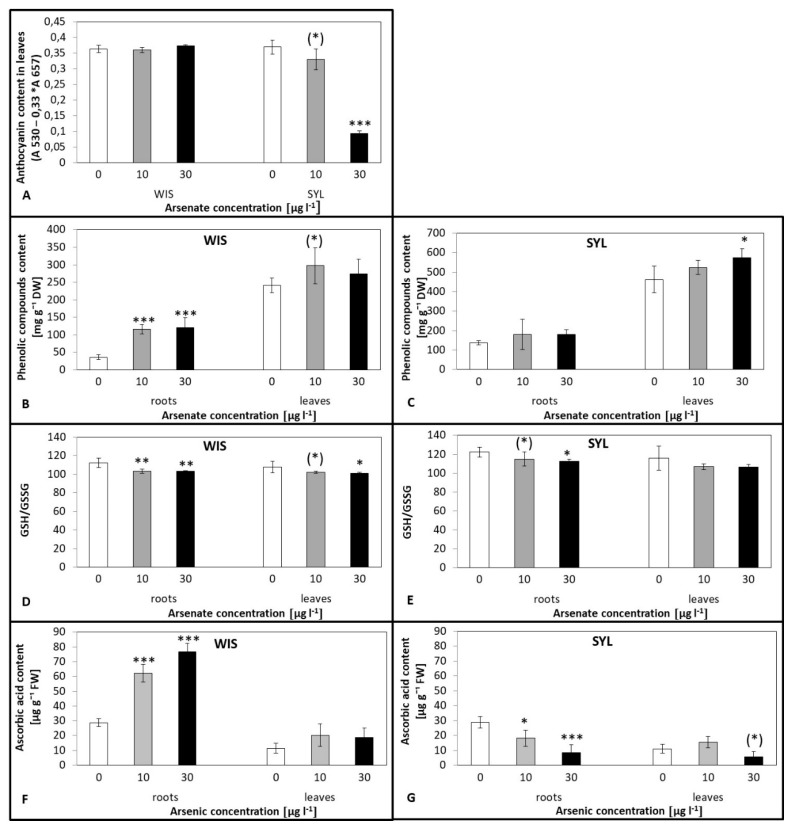
Figure 5.
Effect of arsenic on anthocyanin (A) and phenolics contents (B,C), GSH/GSSG - glutathione forms ratio (D,E), and ascorbate contents (F,G) in two contrasting tobacco genotypes ((A,B,D,F) tolerant N.tabacum cv.Wisconsin; (A,C,E,G) sensitive N. sylvestris). 0, 10, and 30 µg l−1 arsenate treatments. Bars indicate standard deviations. Stars mean statistically significant differences from control at the level α = 0.1 ((*)), 0.05(*), 0.01 (**) or 0.001(***), n = 4–5.