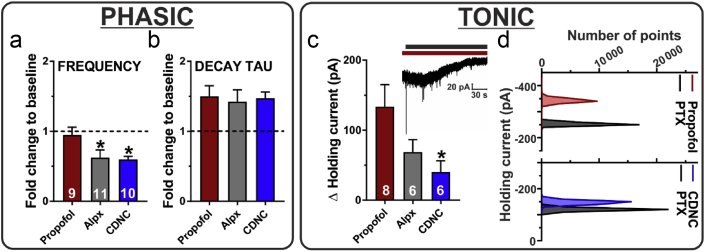
Figure 6.
Comparison of effects of propofol, alphaxalone, and CDNC24 on phasic and tonic GABAergic inhibition in the subiculum of postnatal Days 7–9 rat pups. (a) The decrease in spontaneous inhibitory postsynaptic current (sIPSC) frequency observed after alphaxalone (Alpx) 3 μM or CDNC24 3 μM was significantly greater compared with propofol 10 μM (one-way analysis of variance followed by Dunnett's post hoc: F2,27=4.05; P=0.029; ∗P=0.042 [Alpx] and ∗P=0.030 [CDNC], both vs propofol). (b) All three compounds similarly potentiated sIPSC decay time. (c) The change in holding current after the application of picrotoxin (PTX) was significantly smaller in the CDNC24 group (F2,17=3.81; P=0.043; ∗P=0.031; n=6 neurones, four rats), but not in the Alpx group (P=0.145; n=6 neurones, three rats) compared with the propofol group (n=8 neurones, seven rats). The inset shows an original trace from a representative subicular neurone after propofol (dark red bar) and PTX (black bar) applications. Note the outward shift in the holding current after the application of PTX, which indicates inhibition of tonic γ-aminobutyric acid current. (d) All points count histograms of the same experiment shown in the inset of (c) (top) and a representative neurone in the CDNC24 group (bottom). Results are expressed as mean (standard error of the mean).