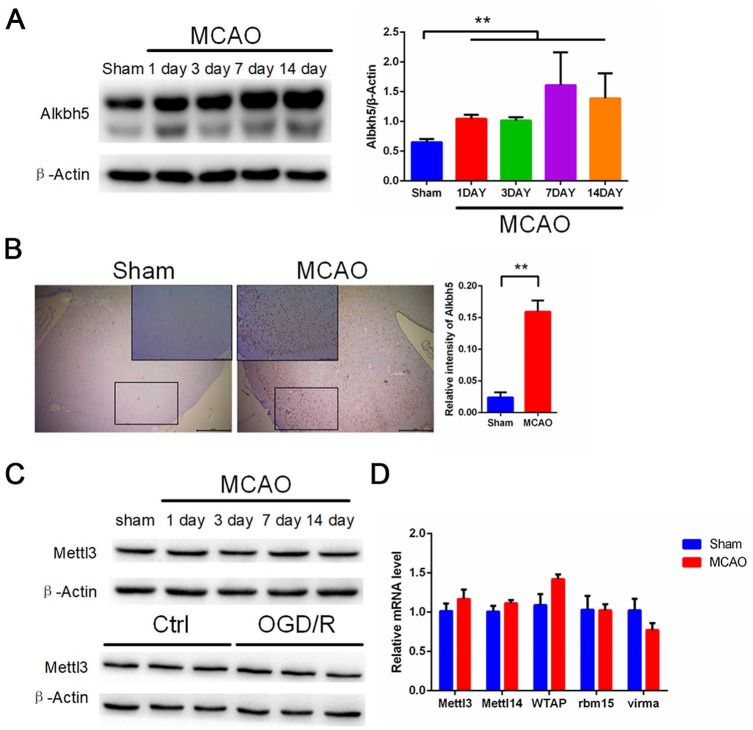
Figure 3.
MCAO and OGD/R induce elevated levels of Alkbh5 both in rat cerebral cortex and primary cerebral cortical neurons. (A) Representative images of Western blots of MCAO-treated rat cerebral cortex. Alkbh5 levels were determined by Western blot (mean ± SEM; n ⩾ 3; **p < 0.01 versus sham). (B) Immunohistochemical results of Alkbh5 in rat cerebral cortex in two indicator groups: tawny staining for Alkbh5 protein and light blue staining for hematoxylin. Scale bar = 50 μm, and the small picture scale bar = 20 μm. Quantification of Alkbh5 was shown (mean ± SEM; n = 3; **p < 0.01 versus Sham). (C) Representative images of Western blots of MCAO treated rat cerebral cortex and OGD/R treated primary neurons. Mettle13 levels were determined by Western blot (mean ± SEM; n = 3; ns p > 0.05 versus Sham or Ctrl). (D) qRT-PCR images of MCAO-treated rat cerebral cortex. Mettl3, Mettl14, WTAP, VIRMA, and RBM15 levels were analyzed by qRT-PCR (mean ± SEM; n = 3; ns p > 0.05 versus Sham).
Ctrl, control; MCAO, middle cerebral artery occlusion; OGD/R, glucose oxygen deprivation/reoxygenation; qRT-PCR, quantitative reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction; SEM, standard error of the mean.