Fig. 1.
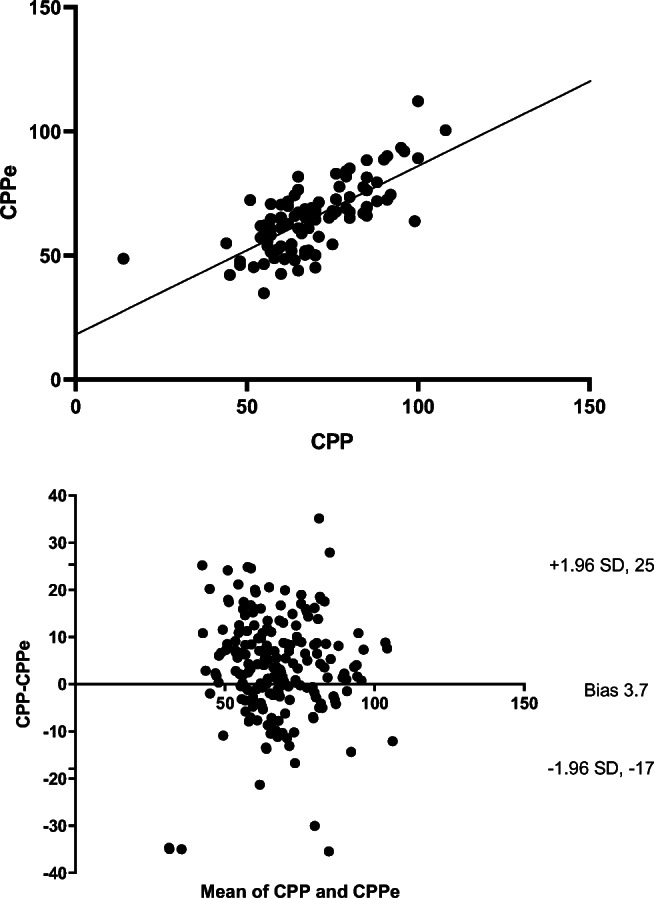
Using patient averaged data, correlation between cerebral perfusion pressure (CPP) and non-invasively estimated cerebral perfusion pressure (CPPe = (mean arterial blood pressure × diastolic flow velocity/mean flow velocity) + 14) was significant (r = 0.78, p ≤ 0.001). The Bland-Altman plot of agreement between the two revealed bias of 3.7 mmHg with 95% limits of agreement − 17, + 25 mmHg
