Fig. 4.
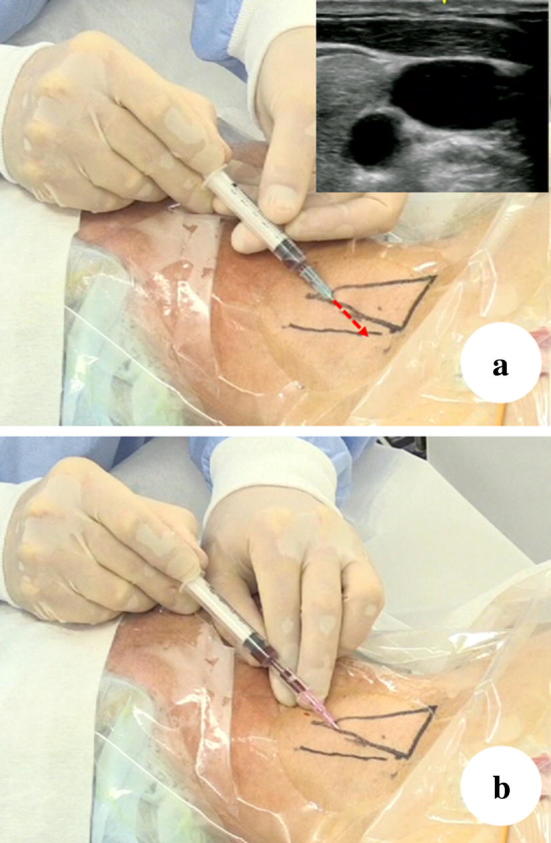
Static approach. The triangle shows the Sedillot’s triangle. The line lateral to the Sedillot’s triangle indicates the IJV location confirmed in an ultrasound image. In some cases, the IJV is located outside of the Sedillot’s triangle. If the operator inserts the needle immediately above the line, which was the IJV location confirmed in an ultrasound image, the sternocleidomastoid muscle (clavicular head) would likely be penetrated, which may cause difficulty in the insertion of the dilator. When enlarging the route of the guidewire through the thick muscle using the dilator, a patient who is awake may feel discomfort and fear. Furthermore, difficulty in the insertion of the dilator may sometimes cause kinks and aberrant movement of the guidewire from the vein. Even the procedure has been performed safely, the patient will complain of discomfort when they move their neck. If the operator chooses the real-time ultrasound-guided approach in this case, the operator can insert the needle on the line at a relatively cephalad portion, which can prevent the penetration of the sternocleidomastoid muscle, rendering it safer
