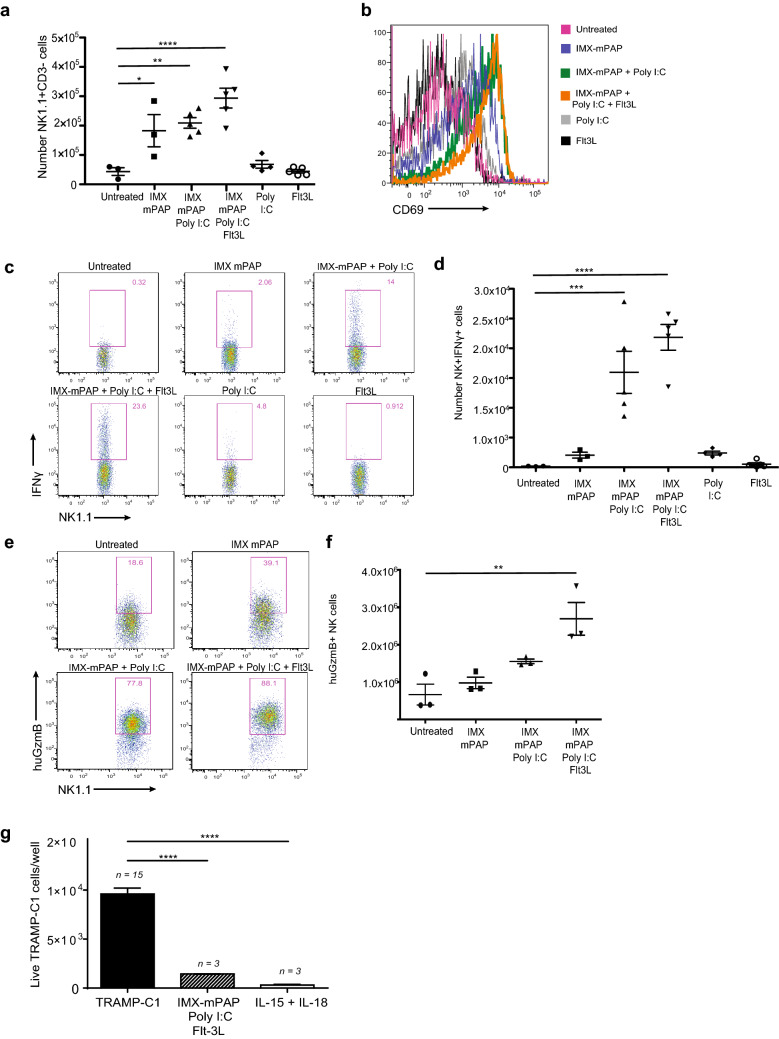
Fig. 3.
Vaccination induces strong phenotypic and functional activation of NK cells that are prepared for tumor elimination. a Enumeration of NK cells. b NK cell activation was assessed using the early activation marker CD69. Representative histograms showing the geometric mean fluorescence intensity of CD69 staining. c Representative profiles of NK cells producing IFNγ (ex vivo) 8 h after priming. d Enumeration of IFNγ-producing NK cells. e Representative profiles of NK cells producing Granzyme B (ex vivo), 24 h after boosting, detected by ICS. f Granzyme B-producing NK cells were enumerated. g in vitro TRAMP-C1 killing assay. n, indicates the number of replicate wells. Data are presented as mean ± SEM where n = 3–5 mice/group from one representative experiment of two equivalent experiments. a, d, f, g Statistical significance was determined using a one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparisons test. p < 0.05*, p < 0.01**, p < 0.001*** and p < 0.0001****. IMX = ISCOMATRIX® adjuvant